HIF-2α regulates proliferation, invasion, and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via VEGF/Notch1 signaling axis after insufficient radiofrequency ablation
- PMID: 36212390
- PMCID: PMC9539942
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.998295
HIF-2α regulates proliferation, invasion, and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via VEGF/Notch1 signaling axis after insufficient radiofrequency ablation
Abstract
Background and aims: Although insufficient radiofrequency ablation (RFA) promotes the recurrence and metastasis of liver cancer, the underlying mechanism remains unclear. This study aimed to investigate the role and mechanism of HIF-2α in hepatocellular carcinoma cells (HCCs) after Insufficient RFA.
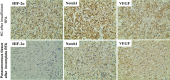
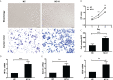
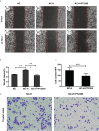
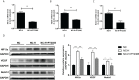
Methods: We established a model of insufficient RFA in MHCC97H hepatoma cells and screened for stable sublines. We inhibited HIF-2α expression in the Insufficient RFA group using PT2385 and assessed the resulting changes in proliferation and biological function of HCCs. Cell viability and proliferation were detected by the MTT method, and scratch and Transwell chamber invasion tests detected migration and invasion abilities of HCCs. The mRNA and protein expression levels of VEGF, HIF-2α, and Notch1 were detected using qPCR, immunofluorescence, and western blotting.
Results: Compared with normal HCCs without RFA treatment, insufficient RFA enhanced the proliferation and invasion abilities of hepatocellular carcinoma subline MHCC97H (P < 0.001), as well as their migration ability (P = 0.046). The HIF-2α-specific inhibitor PT2385 downregulated the migration (P = 0.009) and invasion (P < 0.001) of MHCC97H cells but did not affect cell proliferation (P > 0.05). Insufficient ablation increased the mRNA and protein expression of VEGF, HIF-2α, and Notch1 in HCCs, whereas inhibition of HIF-2α reversed these changes.
Conclusions: Insufficient RFA increases the proliferation, migration, and invasion of HCCs via the HIF-2α/VEGF/Notch1 signaling axis; HIF-2α is a potential target for novel treatments of HCC after insufficient RFA.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; hypoxia-inducible factor-2α; metastasis; radiofrequency ablation; residual carcinoma.
Copyright © 2022 Yang, Chen, Mai and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aberrantly expressed HIF-1α enhances HCC stem cell-like traits via Wnt/β-catenin signaling activation after insufficient radiofrequency ablation.J Cancer Res Ther. 2023 Dec 1;19(6):1517-1524. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.jcrt_1458_21. Epub 2023 Dec 28. J Cancer Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 38156917
-
Incomplete radiofrequency ablation accelerates proliferation and angiogenesis of residual lung carcinomas via HSP70/HIF-1α.Oncol Rep. 2016 Aug;36(2):659-68. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.4858. Epub 2016 Jun 7. Oncol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27278081 Free PMC article.
-
Arsenic trioxide inhibits angiogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma after insufficient radiofrequency ablation via blocking paracrine angiopoietin-1 and angiopoietin-2.Int J Hyperthermia. 2022;39(1):888-896. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2022.2093995. Int J Hyperthermia. 2022. PMID: 35848416
-
Roles of hypoxia-inducible factor in hepatocellular carcinoma under local ablation therapies.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 6;14:1086813. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1086813. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36814489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic response assessment of RFA for HCC: contrast-enhanced US, CT and MRI.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Apr 21;20(15):4160-6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i15.4160. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24764654 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging assessment of residual tumor angiogenesis after insufficient microwave ablation and donafenib adjuvant therapy.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 24;14(1):4557. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-55416-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38402352 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms and therapeutic strategies to combat the recurrence and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma after thermal ablation.J Interv Med. 2023 Oct 18;6(4):160-169. doi: 10.1016/j.jimed.2023.10.004. eCollection 2023 Nov. J Interv Med. 2023. PMID: 38312128 Free PMC article.
-
EPAS1/HIF-2α Acts as an Unanticipated Tumor-Suppressive Role in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma.Int J Gen Med. 2023 May 31;16:2165-2174. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S409874. eCollection 2023. Int J Gen Med. 2023. PMID: 37284036 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet count as a predictor of vascular invasion and extrahepatic metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 18;10(6):e28173. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28173. eCollection 2024 Mar 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38545227 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Results, Risk Factors, and Future Directions of Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Microwave Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2023 May 15;10:733-743. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S409011. eCollection 2023. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2023. PMID: 37215363 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

