[Exosomal FZD10 derived from non-small cell lung cancer cells promotes angiogenesis of human umbilical venous endothelial cells in vitro]
- PMID: 36210708
- PMCID: PMC9550558
- DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2022.09.11
[Exosomal FZD10 derived from non-small cell lung cancer cells promotes angiogenesis of human umbilical venous endothelial cells in vitro]
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effect of exosomal FZD10 derived from non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells on angiogenesis of human umbilical venous endothelial cells (HUVECs) and explore the possible mechanism.
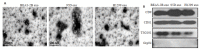
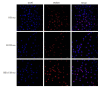
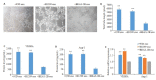
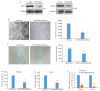
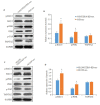
Methods: We analyzed the expression of FZD10 in two NSCLC cell lines (95D and H1299 cells), normal human bronchial epithelial cells (BEAS-2B cells) and their exosomes isolated by ultracentrifugation. Cultured HUVECs were treated with the exosomes derived from NSCLC cells or NSCLC cells transfected with FZD10-siRNA, and the changes in tube formation ability of the cells were analyzed using an in vitro angiogenesis assay. ELISA was performed to determine the concentration of VEGFA and Ang-1 in the conditioned media of HUVECs, and RT-qPCR was used to analyze the mRNA levels of VEGFA and Ang-1 in the HUVECs. The effects of exosomal FZD10 on the activation of PI3K, Erk1/2 and YAP/TAZ signaling pathways were evaluated using Western blotting.
Results: Compared with BEAS-2B cells and their exosomes, 95D and H1299 cells and their exosomes all expressed high levels of FZD10 (P < 0.01). The exosomes derived from 95D and H1299 cells significantly enhanced tube formation ability and increased the expressions of VEGFA and Ang-1 protein and mRNA in HUVECs (P < 0.01), but FZD10 knockdown in 95D and H1299 cells obviously inhibited these effects of the exosomes. Exosomal FZD10 knockdown suppressed the activation of PI3K and Erk1/2 signaling pathways, but had no obvious effect on the activation of YAP/TAZ signaling pathway.
Conclusion: Exosomal FZD10 derived from NSCLC cells promotes HUVEC angiogenesis in vitro, the mechanism of which may involve the activation of PI3K and Erk1/2 signaling pathways.
目的: 探讨非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)细胞外泌体源性FZD10在血管生成中的作用及其机制。
方法: 采用超速离心法分离外泌体,并利用Western blot和RT-qPCR技术分析NSCLC细胞(95D和H1299)、正常人支气管上皮细胞(BEAS-2B)及其外泌体中FZD10的表达;通过转染FZD10-siRNA敲低FZD10表达,用FZD10未敲低和敲低的NSCLC细胞外泌体分别处理HUVEC细胞,利用体外血管生成实验观察其成管能力,采用ELISA和RT-qPCR技术分析血管生成相关因子VEGFA和Ang-1的表达;进一步利用Western blot分析外泌体源性FZD10对信号通路PI3K、Erk1/2和YAP/TAZ激活的影响。
结果: 同BEAS-2B细胞及其外泌体相比较,FZD10在95D和H1299细胞及其外泌体中高表达(P < 0.01);95D和H1299细胞来源的外泌体可促进HUVEC的微管形成及VEGFA、Ang-1的蛋白分泌、mRNA的表达(P < 0.01),但在95D和H1299细胞敲低FZD10后这些效果受到抑制。FZD10的敲低可抑制PI3K、Erk1/2信号通路的激活,但对YAP/TAZ信号通路的影响不显著。
结论: NSCLC细胞外泌体源性FZD10可促进体外血管生成,其机制可能与PI3K、Erk1/2信号通路的激活有关。
Keywords: FZD10; angiogenesis; exosomes; non-small cell lung cancer.
Figures
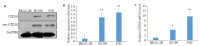
Similar articles
-
Exosomal EGFR and miR-381-3P Mediate HPV-16 E7 Oncoprotein-Induced Angiogenesis of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024 May 15;29(5):189. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2905189. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024. PMID: 38812317
-
Effect of microRNA-135a on Cell Proliferation, Migration, Invasion, Apoptosis and Tumor Angiogenesis Through the IGF-1/PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(4):1431-1446. doi: 10.1159/000479207. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28715819
-
Exosomal circular RNA circ_0074673 regulates the proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells via the microRNA-1200/MEOX2 axis.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):6782-6792. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1967077. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34516311 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal lncRNA SNHG12 promotes angiogenesis and breast cancer progression.Breast Cancer. 2024 Jul;31(4):607-620. doi: 10.1007/s12282-024-01574-6. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Breast Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38833118 Free PMC article.
-
OSCC Exosomes Regulate miR-210-3p Targeting EFNA3 to Promote Oral Cancer Angiogenesis through the PI3K/AKT Pathway.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Jul 8;2020:2125656. doi: 10.1155/2020/2125656. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32695810 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
