Alzheimer's disease: insights from a network medicine perspective
- PMID: 36207441
- PMCID: PMC9546925
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-20404-3
Alzheimer's disease: insights from a network medicine perspective
Abstract
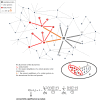
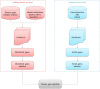
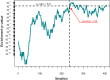
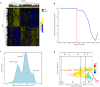
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disease that currently lacks available effective therapy. Thus, identifying novel molecular biomarkers for diagnosis and treatment of AD is urgently demanded. In this study, we exploited tools and concepts of the emerging research area of Network Medicine to unveil a novel putative disease gene signature associated with AD. We proposed a new pipeline, which combines the strengths of two consolidated algorithms of the Network Medicine: DIseAse MOdule Detection (DIAMOnD), designed to predict new disease-associated genes within the human interactome network; and SWItch Miner (SWIM), designed to predict important (switch) genes within the co-expression network. Our integrated computational analysis allowed us to enlarge the set of the known disease genes associated to AD with additional 14 genes that may be proposed as new potential diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets for AD phenotype.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNAs in Alzheimer's disease: Potential diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Apr;148:112681. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112681. Epub 2022 Feb 15. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 35177290 Review.
-
Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis to Identify Alternative Therapeutic Targets for Alzheimer's Disease: Insights from a Synaptic Machinery Perspective.J Mol Neurosci. 2022 Feb;72(2):273-286. doi: 10.1007/s12031-021-01893-9. Epub 2021 Aug 19. J Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 34414562
-
Network Medicine for Alzheimer's Disease and Traditional Chinese Medicine.Molecules. 2018 May 11;23(5):1143. doi: 10.3390/molecules23051143. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29751596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intrinsic-overlapping co-expression module detection with application to Alzheimer's Disease.Comput Biol Chem. 2018 Dec;77:373-389. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2018.10.014. Epub 2018 Nov 9. Comput Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30466046
-
A 3-Gene-Based Diagnostic Signature in Alzheimer's Disease.Eur Neurol. 2022;85(1):6-13. doi: 10.1159/000518727. Epub 2021 Sep 14. Eur Neurol. 2022. PMID: 34521086
Cited by
-
TTD: Therapeutic Target Database describing target druggability information.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jan 5;52(D1):D1465-D1477. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad751. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 37713619 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in expression of VGF, SPECC1L, HLA-DRA and RANBP3L act with APOE E4 to alter risk for late onset Alzheimer's disease.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 28;14(1):14954. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-65010-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38942763 Free PMC article.
-
Alteration of gene expression and protein solubility of the PI 5-phosphatase SHIP2 are correlated with Alzheimer's disease pathology progression.Acta Neuropathol. 2024 Jun 4;147(1):94. doi: 10.1007/s00401-024-02745-7. Acta Neuropathol. 2024. PMID: 38833073 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Caldera M, Buphamalai P, Müller F, Menche J. Interactome-based approaches to human disease. Curr. Opin. Syst. Biol. 2017;3:88–94. doi: 10.1016/j.coisb.2017.04.015. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

