Mechanistic insights into protein folding by the eukaryotic chaperonin complex CCT
- PMID: 36196890
- PMCID: PMC9704529
- DOI: 10.1042/BST20220591
Mechanistic insights into protein folding by the eukaryotic chaperonin complex CCT
Abstract
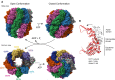
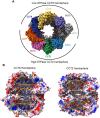
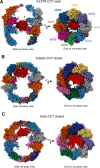
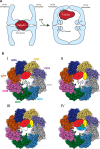
The cytosolic chaperonin CCT is indispensable to eukaryotic life, folding the cytoskeletal proteins actin and tubulin along with an estimated 10% of the remaining proteome. However, it also participates in human diseases such as cancer and viral infections, rendering it valuable as a potential therapeutic target. CCT consists of two stacked rings, each comprised of eight homologous but distinct subunits, that assists the folding of a remarkable substrate clientele that exhibits both broad diversity and specificity. Much of the work in recent years has been aimed at understanding the mechanisms of CCT substrate recognition and folding. These studies have revealed new binding sites and mechanisms by which CCT uses its distinctive subunit arrangement to fold structurally unrelated substrates. Here, we review recent structural insights into CCT-substrate interactions and place them into the broader context of CCT function and its implications for human health.
Keywords: cryo-electron microscopy; molecular chaperones; molecular mechanisms; protein conformation.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structure and function of a protein folding machine: the eukaryotic cytosolic chaperonin CCT.FEBS Lett. 2002 Oct 2;529(1):11-6. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(02)03180-0. FEBS Lett. 2002. PMID: 12354605 Review.
-
TRiC/CCT Chaperonin: Structure and Function.Subcell Biochem. 2019;93:625-654. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-28151-9_19. Subcell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31939165 Review.
-
The Mechanism and Function of Group II Chaperonins.J Mol Biol. 2015 Sep 11;427(18):2919-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2015.04.013. Epub 2015 Apr 30. J Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25936650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutational screen identifies critical amino acid residues of beta-actin mediating interaction between its folding intermediates and eukaryotic cytosolic chaperonin CCT.J Struct Biol. 2001 Aug;135(2):185-97. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.2001.4389. J Struct Biol. 2001. PMID: 11580268
-
Eukaryotic type II chaperonin CCT interacts with actin through specific subunits.Nature. 1999 Dec 9;402(6762):693-6. doi: 10.1038/45294. Nature. 1999. PMID: 10604479
Cited by
-
Reduced ADP off-rate by the yeast CCT2 double mutation T394P/R510H which causes Leber congenital amaurosis in humans.Commun Biol. 2023 Aug 29;6(1):888. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05261-8. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 37644231 Free PMC article.
-
Hsp90, a team player in protein quality control and the stress response in bacteria.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2024 Jun 27;88(2):e0017622. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.00176-22. Epub 2024 Mar 27. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38534118 Review.
-
STYXL1 regulates CCT complex assembly and flagellar tubulin folding in sperm formation.Nat Commun. 2024 Jan 2;15(1):44. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44337-1. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38168070 Free PMC article.
-
Prefoldin Subunits and Its Associate Partners: Conservations and Specificities in Plants.Plants (Basel). 2024 Feb 18;13(4):556. doi: 10.3390/plants13040556. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38498526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Epithelial and Endothelial Barriers by Molecular Chaperones.Cells. 2024 Feb 21;13(5):370. doi: 10.3390/cells13050370. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38474334 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

