Bidirectional Effect of IFN-γ on Th17 Responses in Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis
- PMID: 36188211
- PMCID: PMC9521044
- DOI: 10.3389/fopht.2022.831084
Bidirectional Effect of IFN-γ on Th17 Responses in Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis
Abstract
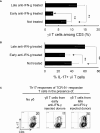
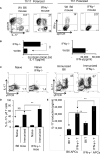
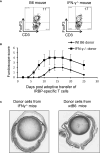
Pro- and ant-inflammatory effects of IFN-γ have been repeatedly found in various immune responses, including cancer and autoimmune diseases. In a previous study we showed that the timing of treatment determines the effect of adenosine-based immunotherapy. In this study we examined the role of IFN-γ in pathogenic Th17 responses in experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU). We observed that IFN-γ has a bidirectional effect on Th17 responses, when tested both in vitro and in vivo. Anti-IFN-γ antibody inhibits Th17 responses when applied in the initial phase of the immune response; however, it enhances the Th17 response if administered in a later phase of EAU. In the current study we showed that IFN-γ is an important immunomodulatory molecule in γδ T cell activation, as well as in Th17 responses. These results should advance our understanding of the regulation of Th17 responses in autoimmunity.
Keywords: IFN-gamma; Th17; autoimmunity; experimental autoimmune uveitis; gamma delta T cell.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Role of Adenosine in γδ T-Cell Regulation of Th17 Responses in Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis.Biomolecules. 2023 Sep 22;13(10):1432. doi: 10.3390/biom13101432. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37892114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activated γδ T Cells Promote Dendritic Cell Maturation and Exacerbate the Development of Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis (EAU) in Mice.Immunol Invest. 2021 Feb;50(2-3):164-183. doi: 10.1080/08820139.2020.1716786. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Immunol Invest. 2021. PMID: 31985304
-
An A2B Adenosine Receptor Agonist Promotes Th17 Autoimmune Responses in Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis (EAU) via Dendritic Cell Activation.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 6;10(7):e0132348. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132348. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26147733 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine receptor activation in the Th17 autoimmune responses of experimental autoimmune uveitis.Cell Immunol. 2019 May;339:24-28. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2018.09.004. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Cell Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30249343 Review.
-
Timing Effect of Adenosine-Directed Immunomodulation on Mouse Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis.J Immunol. 2021 Jul 1;207(1):153-161. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2100182. Epub 2021 Jun 14. J Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34127521 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Human in vitro-induced IL-17A+ CD8+ T-cells exert pro-inflammatory effects on synovial fibroblasts.Clin Exp Immunol. 2023 Dec 11;214(1):103-119. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxad068. Clin Exp Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37367825 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of retinal immune regulation and blood-retinal barrier function during experimental autoimmune uveitis.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 28;14(1):20033. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68401-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39198470 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Adenosine in γδ T-Cell Regulation of Th17 Responses in Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis.Biomolecules. 2023 Sep 22;13(10):1432. doi: 10.3390/biom13101432. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37892114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of the STAT4 Gene rs7574865 Polymorphism with IFN-γ Levels in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Genes (Basel). 2023 Feb 21;14(3):537. doi: 10.3390/genes14030537. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36980810 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokines in PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitor adverse events and implications for the treatment of uveitis.BMC Ophthalmol. 2024 Jul 29;24(1):312. doi: 10.1186/s12886-024-03575-7. BMC Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39075390 Free PMC article. Review.

