Acute and inherited piRNA-mediated silencing in a rde-3 ribonucleotidyltransferase mutant
- PMID: 36188099
- PMCID: PMC9520340
- DOI: 10.17912/micropub.biology.000638
Acute and inherited piRNA-mediated silencing in a rde-3 ribonucleotidyltransferase mutant
Abstract
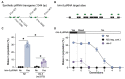
We recently developed a piRNA-based silencing assay (piRNAi) to study small-RNA mediated epigenetic silencing: acute gene silencing is induced by synthetic piRNAs expressed from extra-chromosomal array and transgenerational inheritance can be quantified after array loss. The assay allows inheritance assays by injecting piRNAs directly into mutant animals and targeting endogenous genes ( e.g. , him-5 and him-8 ) with obvious phenotypes (increased male frequency). Here we demonstrate the piRNAi assay by quantifying acute and inherited silencing in the ribonucleotidyltransferase rde-3 (ne3370) mutant. In the absence of rde-3, acute silencing was reduced but still detectable, whereas inherited silencing was abolished.
Copyright: © 2022 by the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PiWi RNA in Neurodevelopment and Neurodegenerative Disorders.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2022;15(3):517-531. doi: 10.2174/1874467214666210629164535. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34212832 Review.
-
The piRNA targeting rules and the resistance to piRNA silencing in endogenous genes.Science. 2018 Feb 2;359(6375):587-592. doi: 10.1126/science.aao2840. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Science. 2018. PMID: 29420292 Free PMC article.
-
Profiles of piRNA abundances at emerging or established piRNA loci are determined by local DNA sequences.RNA Biol. 2013 Aug;10(8):1233-9. doi: 10.4161/rna.25756. Epub 2013 Jul 15. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 23880829 Free PMC article.
-
PIWI-Interacting RNA: Its Biogenesis and Functions.Annu Rev Biochem. 2015;84:405-33. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-060614-034258. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Annu Rev Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25747396 Review.
-
The capacity of target silencing by Drosophila PIWI and piRNAs.RNA. 2014 Dec;20(12):1977-86. doi: 10.1261/rna.046300.114. Epub 2014 Oct 21. RNA. 2014. PMID: 25336588 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Interactions of piRNAs with the mRNA of Candidate Genes in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Jul 23;45(7):6140-6153. doi: 10.3390/cimb45070387. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37504303 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashe A, Sapetschnig A, Weick EM, Mitchell J, Bagijn MP, Cording AC, Doebley AL, Goldstein LD, Lehrbach NJ, Le Pen J, Pintacuda G, Sakaguchi A, Sarkies P, Ahmed S, Miska EA. piRNAs can trigger a multigenerational epigenetic memory in the germline of C. elegans. Cell. 2012 Jun 25;150(1):88–99. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.06.018. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
