The moss-specific transcription factor PpERF24 positively modulates immunity against fungal pathogens in Physcomitrium patens
- PMID: 36186018
- PMCID: PMC9520294
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.908682
The moss-specific transcription factor PpERF24 positively modulates immunity against fungal pathogens in Physcomitrium patens
Abstract
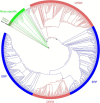
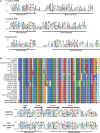
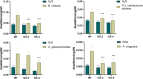
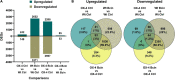
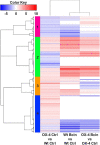
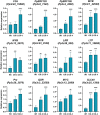
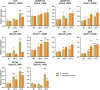
APETALA2/ethylene response factors (AP2/ERFs) transcription factors (TFs) have greatly expanded in land plants compared to algae. In angiosperms, AP2/ERFs play important regulatory functions in plant defenses against pathogens and abiotic stress by controlling the expression of target genes. In the moss Physcomitrium patens, a high number of members of the ERF family are induced during pathogen infection, suggesting that they are important regulators in bryophyte immunity. In the current study, we analyzed a P. patens pathogen-inducible ERF family member designated as PpERF24. Orthologs of PpERF24 were only found in other mosses, while they were absent in the bryophytes Marchantia polymorpha and Anthoceros agrestis, the vascular plant Selaginella moellendorffii, and angiosperms. We show that PpERF24 belongs to a moss-specific clade with distinctive amino acids features in the AP2 domain that binds to the DNA. Interestingly, all P. patens members of the PpERF24 subclade are induced by fungal pathogens. The function of PpERF24 during plant immunity was assessed by an overexpression approach and transcriptomic analysis. Overexpressing lines showed increased defenses to infection by the fungal pathogens Botrytis cinerea and Colletotrichum gloeosporioides evidenced by reduced cellular damage and fungal biomass compared to wild-type plants. Transcriptomic and RT-qPCR analysis revealed that PpERF24 positively regulates the expression levels of defense genes involved in transcriptional regulation, phenylpropanoid and jasmonate pathways, oxidative burst and pathogenesis-related (PR) genes. These findings give novel insights into potential mechanism by which PpERF24 increases plant defenses against several pathogens by regulating important players in plant immunity.
Keywords: AP2/ERF; Physcomitrium patens; defense; pathogens; transcription factor.
Copyright © 2022 Reboledo, Agorio, Vignale, Alvarez and Ponce De León.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcriptional profiling reveals conserved and species-specific plant defense responses during the interaction of Physcomitrium patens with Botrytis cinerea.Plant Mol Biol. 2021 Nov;107(4-5):365-385. doi: 10.1007/s11103-021-01116-0. Epub 2021 Feb 1. Plant Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33521880
-
Physcomitrium patens Infection by Colletotrichum gloeosporioides: Understanding the Fungal-Bryophyte Interaction by Microscopy, Phenomics and RNA Sequencing.J Fungi (Basel). 2021 Aug 22;7(8):677. doi: 10.3390/jof7080677. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34436216 Free PMC article.
-
Moss transcription factors regulating development and defense responses to stress.J Exp Bot. 2022 Jul 16;73(13):4546-4561. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erac055. J Exp Bot. 2022. PMID: 35167679 Review.
-
Botrytis cinerea Transcriptome during the Infection Process of the Bryophyte Physcomitrium patens and Angiosperms.J Fungi (Basel). 2020 Dec 28;7(1):11. doi: 10.3390/jof7010011. J Fungi (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33379257 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptation Mechanisms in the Evolution of Moss Defenses to Microbes.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Mar 15;8:366. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00366. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28360923 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Plant disease resistance outputs regulated by AP2/ERF transcription factor family.Stress Biol. 2024 Jan 2;4(1):2. doi: 10.1007/s44154-023-00140-y. Stress Biol. 2024. PMID: 38163824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The evolution of plant responses underlying specialized metabolism in host-pathogen interactions.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2024 Nov 18;379(1914):20230370. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2023.0370. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39343011 Review.
-
Genome-wide identification and molecular characterization of the AP2/ERF superfamily members in sand pear (Pyrus pyrifolia).BMC Genomics. 2023 Jan 19;24(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-09104-4. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36658499 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of AP2/ERF gene family in Coptis Chinensis Franch reveals its role in tissue-specific accumulation of benzylisoquinoline alkaloids.BMC Genomics. 2024 Oct 16;25(1):972. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10883-1. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39415101 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashton N. W., Cove D. (1977). The isolation and preliminary characterization of auxotrophic and analogue resistant mutants of the moss, Physcomitrella patens. Mol. Genet. Genomics 154 87–95. 10.1007/BF00265581 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

