Highly tailorable gellan gum nanoparticles as a platform for the development of T cell activator systems
- PMID: 36180901
- PMCID: PMC9523970
- DOI: 10.1186/s40824-022-00297-z
Highly tailorable gellan gum nanoparticles as a platform for the development of T cell activator systems
Abstract
Background: T cell priming has been shown to be a powerful immunotherapeutic approach for cancer treatment in terms of efficacy and relatively weak side effects. Systems that optimize the stimulation of T cells to improve therapeutic efficacy are therefore in constant demand. A way to achieve this is through artificial antigen presenting cells that are complexes between vehicles and key molecules that target relevant T cell subpopulations, eliciting antigen-specific T cell priming. In such T cell activator systems, the vehicles chosen to deliver and present the key molecules to the targeted cell populations are of extreme importance. In this work, a new platform for the creation of T cell activator systems based on highly tailorable nanoparticles made from the natural polymer gellan gum (GG) was developed and validated.
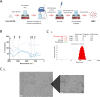
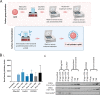
Methods: GG nanoparticles were produced by a water in oil emulsion procedure, and characterized by dynamic light scattering, high resolution scanning electronic microscopy and water uptake. Their biocompatibility with cultured cells was assessed by a metabolic activity assay. Surface functionalization was performed with anti-CD3/CD28 antibodies via EDC/NHS or NeutrAvidin/Biotin linkage. Functionalized particles were tested for their capacity to stimulate CD4+ T cells and trigger T cell cytotoxic responses.
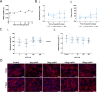
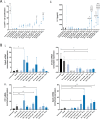
Results: Nanoparticles were approximately 150 nm in size, with a stable structure and no detectable cytotoxicity. Water uptake originated a weight gain of up to 3200%. The functional antibodies did efficiently bind to the nanoparticles, as confirmed by SDS-PAGE, which then targeted the desired CD4+ populations, as confirmed by confocal microscopy. The developed system presented a more sustained T cell activation over time when compared to commercial alternatives. Concurrently, the expression of higher levels of key cytotoxic pathway molecules granzyme B/perforin was induced, suggesting a greater cytotoxic potential for future application in adoptive cancer therapy.
Conclusions: Our results show that GG nanoparticles were successfully used as a highly tailorable T cell activator system platform capable of T cell expansion and re-education.
Keywords: Cytotoxic T cells; Gellan gum; Nanoparticles; T cell stimulation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Daniel Barreira Rodrigues and several other authors have the patent hydrogel-like particles, methods ans uses thereof pending to association for the advancement of tissue engineering and cell based technologies & therapies a4tec – associação.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The effect of artificial antigen-presenting cells with preclustered anti-CD28/-CD3/-LFA-1 monoclonal antibodies on the induction of ex vivo expansion of functional human antitumor T cells.Haematologica. 2008 Oct;93(10):1523-34. doi: 10.3324/haematol.12521. Epub 2008 Aug 25. Haematologica. 2008. PMID: 18728033
-
Gellan gum incorporating titanium dioxide nanoparticles biofilm as wound dressing: Physicochemical, mechanical, antibacterial properties and wound healing studies.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019 Oct;103:109770. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2019.109770. Epub 2019 May 18. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019. PMID: 31349525
-
Erratum: Preparation of Poly(pentafluorophenyl acrylate) Functionalized SiO2 Beads for Protein Purification.J Vis Exp. 2019 Apr 30;(146). doi: 10.3791/6328. J Vis Exp. 2019. PMID: 31038480
-
S-protected gellan gum: Decisive approach towards mucoadhesive antimicrobial vaginal films.Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Jun 1;130:148-157. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.02.092. Epub 2019 Feb 16. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019. PMID: 30779984
-
Nanoscale artificial antigen presenting cells for cancer immunotherapy.Mol Immunol. 2018 Jun;98:13-18. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2018.02.016. Epub 2018 Mar 7. Mol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29525074 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advancements in Biomaterials for Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Immunotherapy.Biomater Res. 2024 Jul 15;28:0045. doi: 10.34133/bmr.0045. eCollection 2024. Biomater Res. 2024. PMID: 39011521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LCST/UCST behavior of polysaccharides for hydrogel fabrication.RSC Adv. 2024 Nov 11;14(48):35754-35768. doi: 10.1039/d4ra06240j. eCollection 2024 Nov 4. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39529738 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
- ERC-2018-STG-805411/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- SFRH/BD/119756/2016/Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia/ Ministério da Ciência, Tecnologia, e Ensino Superior
- IF/00347/2015/Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia/ Ministério da Ciência, Tecnologia, e Ensino Superior
- PD/169/2013/Fundo Social Europeu através do Programa Operacional do Capital Humano
- NORTE-08-5369-FSE-000037/Fundo Social Europeu através do Programa Operacional do Capital Humano
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

