Downregulation of deubiquitinating enzyme USP25 promotes the development of allergic rhinitis by enhancing TSLP signaling in the nasal epithelium
- PMID: 36177892
- PMCID: PMC9551407
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12863
Downregulation of deubiquitinating enzyme USP25 promotes the development of allergic rhinitis by enhancing TSLP signaling in the nasal epithelium
Abstract
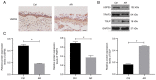
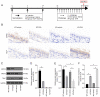
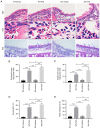
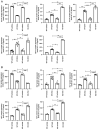
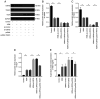
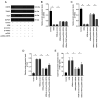
Ubiquitin‑specific peptidase 25 (USP25) is a key deubiquitylase belonging to the USP superfamily that is primarily involved in inflammation and the immune response. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) is an epithelial‑derived cytokine that is regarded as the master switch that initiates and maintains the type 2 immune response in allergic rhinitis (AR). However, the molecular mechanisms by which USP25 regulates TSLP signaling in the nasal epithelium in AR remain unclear. The present study assessed the protein expression levels of USP25 in the nasal epithelium of patients with AR. Moreover, USP25 knockout (KO) and wild‑type (WT) mice were treated with ovalbumin (OVA) to establish a model of AR. The results of western blotting and immunohistochemistry in the present study demonstrated that the protein expression levels of USP25 were significantly decreased in the nasal mucosa of patients with AR and AR mice, whereas the protein expression levels of TSLP were significantly increased. Allergic inflammation was more severe in USP25 KO mice compared with WT mice exposed to OVA, as demonstrated by increased nose scratching and sneezing, increased eosinophil infiltration, goblet cell hyperplasia and enhanced T helper type 2 (Th2) cytokine production. The results of in vitro experiments demonstrated that silencing or overexpression of USP25 decreased or increased TNF receptor‑associated factor 3 (TRAF3) protein expression levels, respectively, in human nasal epithelial cells, whereas TSLP protein expression levels were negatively associated with the expression of USP25 and TRAF3. In summary, USP25 downregulation enhanced TSLP signaling in the nasal mucosal epithelium via decreased TRAF3 expression, thereby exacerbating inflammation in AR. Therefore, USP25 may act as a novel therapeutic target in AR.
Keywords: allergic rhinitis; deubiquitylase; epithelial‑derived cytokine; thymic stromal lymphopoietin; ubiquitin‑specific peptidase 25.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Against NF-κB/thymic stromal lymphopoietin signaling pathway, catechin alleviates the inflammation in allergic rhinitis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2018 Aug;61:241-248. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.06.011. Epub 2018 Jun 9. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29894863
-
Murine allergic rhinitis and nasal Th2 activation are mediated via TSLP- and IL-33-signaling pathways.Int Immunol. 2016 Feb;28(2):65-76. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxv055. Epub 2015 Oct 1. Int Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26428949 Free PMC article.
-
Histamine H4 receptor regulates Th2-cytokine profile through thymic stromal lymphopoietin in allergic rhinitis.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2019 Jun;276(6):1655-1661. doi: 10.1007/s00405-019-05369-w. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2019. PMID: 30848348
-
Nasal Epithelial Barrier Integrity and Tight Junctions Disruption in Allergic Rhinitis: Overview and Pathogenic Insights.Front Immunol. 2021 May 21;12:663626. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.663626. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34093555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TSLP as druggable target - a silver-lining for atopic diseases?Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Jan;217:107648. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107648. Epub 2020 Aug 3. Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 32758645 Review.
Cited by
-
Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin (TSLP), Its Isoforms and the Interplay with the Epithelium in Allergy and Asthma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 12;24(16):12725. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612725. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37628907 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brożek JL, Bousquet J, Agache I, Agarwal A, Bachert C, Bosnic-Anticevich S, Brignardello-Petersen R, Canonica GW, Casale T, Chavannes NH, et al. Allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma (ARIA) guidelines-2016 revision. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;140:950–958. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.03.050. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

