Interaction of HDAC2 with SARS-CoV-2 NSP5 and IRF3 Is Not Required for NSP5-Mediated Inhibition of Type I Interferon Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 36173315
- PMCID: PMC9603796
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.02322-22
Interaction of HDAC2 with SARS-CoV-2 NSP5 and IRF3 Is Not Required for NSP5-Mediated Inhibition of Type I Interferon Signaling Pathway
Abstract
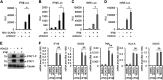
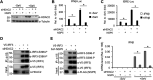
Over the last 2 years, several global virus-host interactome studies have been published with SARS-CoV-2 proteins with the purpose of better understanding how specific viral proteins can subvert or utilize different cellular processes to promote viral infection and pathogenesis. However, most of the virus-host protein interactions have not yet been confirmed experimentally, and their biological significance is largely unknown. The goal of this study was to verify the interaction of NSP5, the main protease of SARS-CoV-2, with the host epigenetic factor histone deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) and test if HDAC2 is required for NSP5-mediated inhibition of the type I interferon signaling pathway. Our results show that NSP5 can significantly reduce the expression of a subset of immune response genes such as IL-6, IL-1β, and IFNβ, which requires NSP5's protease activity. We also found that NSP5 can inhibit Sendai virus-, RNA sensor-, and DNA sensor-mediated induction of IFNβ promoter, block the IFN response pathway, and reduce the expression of IFN-stimulated genes. We also provide evidence for HDAC2 interacting with IRF3, and NSP5 can abrogate their interaction by binding to both IRF3 and HDAC2. In addition, we found that HDAC2 plays an inhibitory role in the regulation of IFNβ and IFN-induced promoters, but our results indicate that HDAC2 is not involved in NSP5-mediated inhibition of IFNβ gene expression. Taken together, our data show that NSP5 interacts with HDAC2 but NSP5 inhibits the IFNβ gene expression and interferon-signaling pathway in an HDAC2-independent manner. IMPORTANCE SARS-CoV-2 has developed multiple strategies to antagonize the host antiviral response, such as blocking the IFN signaling pathway, which favors the replication and spreading of the virus. A recent SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction mapping revealed that the main viral protease NSP5 interacts with the host epigenetic factor HDAC2, but the interaction was not confirmed experimentally and its biological importance remains unclear. Here, we not only verified the interaction of HDAC2 with NSP5, but we also found that HDAC2 also binds to IRF3, and NSP5 can disrupt the IRF3-HDAC2 complex. Furthermore, our results show that NSP5 can efficiently repress the IFN signaling pathway regardless of whether viral infections, RNA, or DNA sensors activated it. However, our data indicate that HDAC2 is not involved in NSP5-mediated inhibition of IFNβ promoter induction and IFNβ gene expression.
Keywords: HDAC2; NSP5; SARS-CoV-2; interferons; protein-protein interactions; type I IFN signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MERS-CoV-nsp5 expression in human epithelial BEAS 2b cells attenuates type I interferon production by inhibiting IRF3 nuclear translocation.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Oct 12;81(1):433. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05458-y. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39395053 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 main protease suppresses type I interferon production by preventing nuclear translocation of phosphorylated IRF3.Int J Biol Sci. 2021 Apr 10;17(6):1547-1554. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.59943. eCollection 2021. Int J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33907518 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 suppresses IFNβ production mediated by NSP1, 5, 6, 15, ORF6 and ORF7b but does not suppress the effects of added interferon.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Aug 26;17(8):e1009800. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009800. eCollection 2021 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34437657 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional and Non-Transcriptional Activation, Posttranslational Modifications, and Antiviral Functions of Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 and Viral Antagonism by the SARS-Coronavirus.Viruses. 2021 Mar 29;13(4):575. doi: 10.3390/v13040575. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33805458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coronaviral PLpro proteases and the immunomodulatory roles of conjugated versus free Interferon Stimulated Gene product-15 (ISG15).Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Dec;132:16-26. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.06.005. Epub 2022 Jun 25. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35764457 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Innate Immune Evasion of PRRSV nsp11 through Degradation of the HDAC2 by Its Endoribonuclease Activity.Viruses. 2024 Apr 25;16(5):678. doi: 10.3390/v16050678. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38793560 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 NSP5 antagonizes MHC II expression by subverting histone deacetylase 2.J Cell Sci. 2024 May 15;137(10):jcs262172. doi: 10.1242/jcs.262172. Epub 2024 May 22. J Cell Sci. 2024. PMID: 38682259 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic modulation of myeloid cell functions in HIV and SARS-CoV-2 infection.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Feb 24;51(1):342. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09266-2. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38400997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Control of Innate Immunity: Consequences of Acute Respiratory Virus Infection.Viruses. 2024 Jan 27;16(2):197. doi: 10.3390/v16020197. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38399974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MERS-CoV-nsp5 expression in human epithelial BEAS 2b cells attenuates type I interferon production by inhibiting IRF3 nuclear translocation.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Oct 12;81(1):433. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05458-y. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39395053 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ren LL, Wang YM, Wu ZQ, Xiang ZC, Guo L, Xu T, Jiang YZ, Xiong Y, Li YJ, Li XW, Li H, Fan GH, Gu XY, Xiao Y, Gao H, Xu JY, Yang F, Wang XM, Wu C, Chen L, Liu YW, Liu B, Yang J, Wang XR, Dong J, Li L, Huang CL, Zhao JP, Hu Y, Cheng ZS, Liu LL, Qian ZH, Qin C, Jin Q, Cao B, Wang JW. 2020. Identification of a novel coronavirus causing severe pneumonia in human: a descriptive study. Chin Med J (Engl) 133:1015–1024. doi:10.1097/CM9.0000000000000722. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song J, Zhao X, Huang B, Shi W, Lu R, Niu P, Zhan F, Ma X, Wang D, Xu W, Wu G, Gao GF, Tan W, China Novel Coronavirus Investigating and Research Team . 2020. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med 382:727–733. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lu R, Zhao X, Li J, Niu P, Yang B, Wu H, Wang W, Song H, Huang B, Zhu N, Bi Y, Ma X, Zhan F, Wang L, Hu T, Zhou H, Hu Z, Zhou W, Zhao L, Chen J, Meng Y, Wang J, Lin Y, Yuan J, Xie Z, Ma J, Liu WJ, Wang D, Xu W, Holmes EC, Gao GF, Wu G, Chen W, Shi W, Tan W. 2020. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 395:565–574. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

