The reversion of DNA methylation-induced miRNA silence via biomimetic nanoparticles-mediated gene delivery for efficient lung adenocarcinoma therapy
- PMID: 36171576
- PMCID: PMC9516831
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-022-01651-4
The reversion of DNA methylation-induced miRNA silence via biomimetic nanoparticles-mediated gene delivery for efficient lung adenocarcinoma therapy
Abstract
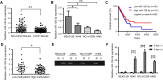
Background: Lung cancer is one of the fatal cancers worldwide, and over 60% of patients are lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). Our clinical data demonstrated that DNA methylation of the promoter region of miR-126-3p was upregulated, which led to the decreased expression of miR-126-3p in 67 cases of lung cancer tissues, implying that miR-126-3p acted as a tumor suppressor. Transduction of miR-126-3p is a potential therapeutic strategy for treating LUAD, yet the physiological environment and properties of miRNA challenge current transduction approaches.
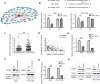
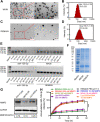
Methods: We evaluated the expression of miR-126-3p in 67 pairs of lung cancer tissues and the corresponding adjacent non-tumorous tissues by Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). The relationship between the overall survival of lung cancer patients and miR-126-3p was analyzed by the Cancer Genome Atlas cohort database (Oncolnc, http://www.oncolnc.org ). We analyzed DNA methylation Methylation-specific PCR (MSP) analysis. To determine whether ADAM9 is the direct target of miR-126-3p, we performed the 3'-UTR luciferase reporter assay. The protein levels in the cells or tissues were evaluated with western blotting (WB) analysis. The biodistribution of nanoparticles were monitored by in vivo tracking system.
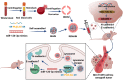
Results: We describe the development of novel stealth and matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2)-activated biomimetic nanoparticles, which are constructed using MMP2-responsive peptides to bind the miR-126-3p (known as MAIN), and further camouflaged with red blood cell (RBC) membranes (hence named REMAIN). REMAIN was able to effectively transduce miRNA into lung cancer cells and release them via MMP2 responsiveness. Additionally, REMAIN possessed the advantages of the natural RBC membrane, including extended circulation time, lower toxicity, better biocompatibility, and immune escape. Moreover, in vitro and in vivo results demonstrated that REMAIN effectively induced apoptosis of lung cancer cells and inhibited LUAD development and progression by targeting ADAM9.
Conclusion: The novel style of stealth and MMP2-activated biomimetic nanoparticles show great potential in miRNA delivery.
Keywords: Biomimetic nanoparticles; DNA methylation; Lung adenocarcinoma; MMP2; MicroRNA.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Upregulation of the Coatomer Protein Complex Subunit beta 2 (COPB2) Gene Targets microRNA-335-3p in NCI-H1975 Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells to Promote Cell Proliferation and Migration.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Jan 31;26:e918382. doi: 10.12659/MSM.918382. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32004259 Free PMC article.
-
Promoter methylation-regulated miR-148a-3p inhibits lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) progression by targeting MAP3K9.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022 Nov;43(11):2946-2955. doi: 10.1038/s41401-022-00893-8. Epub 2022 Apr 6. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022. PMID: 35388129 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated analysis of miRNAs and DNA methylation identifies miR-132-3p as a tumor suppressor in lung adenocarcinoma.Thorac Cancer. 2020 Aug;11(8):2112-2124. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13497. Epub 2020 Jun 4. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32500672 Free PMC article.
-
miR-181a/b therapy in lung cancer: reality or myth?Mol Oncol. 2019 Jan;13(1):9-25. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12420. Epub 2019 Jan 3. Mol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30548184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiRNAs in Lung Adenocarcinoma: Role, Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 27;24(17):13302. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713302. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686110 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cell Membrane-Camouflaged Nanoparticles Mediated Nucleic Acids Delivery.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Dec 28;18:8001-8021. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S433737. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 38164266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomimetic Nano-Drug Delivery System: An Emerging Platform for Promoting Tumor Treatment.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Jan 18;19:571-608. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S442877. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38260239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression patterns of platinum resistance-related genes in lung adenocarcinoma and related clinical value models.Front Genet. 2022 Nov 24;13:993322. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.993322. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36506331 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into nanosystems for non-small-cell lung cancer: diagnosis and treatment.RSC Adv. 2023 Jun 28;13(28):19540-19564. doi: 10.1039/d3ra03099g. eCollection 2023 Jun 22. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 37388143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic and therapeutic roles of SETD2 in cutaneous melanoma.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Jun 5;16(11):9692-9708. doi: 10.18632/aging.205894. Epub 2024 Jun 5. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38843391 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

