DSTYK inhibition increases the sensitivity of lung cancer cells to T cell-mediated cytotoxicity
- PMID: 36169652
- PMCID: PMC9524203
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20220726
DSTYK inhibition increases the sensitivity of lung cancer cells to T cell-mediated cytotoxicity
Abstract
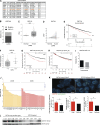
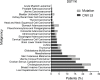
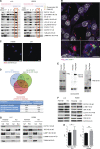
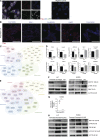
Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. We identify DSTYK, a dual serine/threonine and tyrosine non-receptor protein kinase, as a novel actionable target altered in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). We also show DSTYK's association with a lower overall survival (OS) and poorer progression-free survival (PFS) in multiple patient cohorts. Abrogation of DSTYK in lung cancer experimental systems prevents mTOR-dependent cytoprotective autophagy, impairs lysosomal biogenesis and maturation, and induces accumulation of autophagosomes. Moreover, DSTYK inhibition severely affects mitochondrial fitness. We demonstrate in vivo that inhibition of DSTYK sensitizes lung cancer cells to TNF-α-mediated CD8+-killing and immune-resistant lung tumors to anti-PD-1 treatment. Finally, in a series of lung cancer patients, DSTYK copy number gain predicts lack of response to the immunotherapy. In summary, we have uncovered DSTYK as new therapeutic target in lung cancer. Prioritization of this novel target for drug development and clinical testing may expand the percentage of NSCLC patients benefiting from immune-based treatments.
© 2022 Valencia et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: R. Thomas reported grants from Roche, personal fees from PearlRiver, and “other” from PearlRiver, Centessa, and Epiphanes outside the submitted work. J. Frigola reported grants from Merck Healthcare KGaA during the conduct of the study. A. Calvo reported grants from AstraZeneca and PharmaMar outside the submitted work. E. Felip reported other from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, F. Hoffman - La Roche, GlaxoSmithKline, Ipsen, Janssen, Medical Trends, Medscape, Merck KGaA, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, PeerVoice, Peptomyc, Pfizer, Sanofi, Springer, Takeda, TouchTime, Fundación Merck Salud, Grant for Oncology Innovation and Merck, Healthcare KGaA, and Grifols (Independent Member of the Board) outside the submitted work. I. Melero reported personal fees from AstraZeneca, Pharmamar, Roche, and Genmab; grants from AstraZeneca, BMS, Genmab, and Roche; and personal fees from Merus, F-star, Numab, Amunix, Third Rock, and Pieris outside the submitted work. L.M. Montuenga reported grants from AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Serum. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures
Comment in
-
Eating away T cell responses in lung cancer.J Exp Med. 2022 Dec 5;219(12):e20221449. doi: 10.1084/jem.20221449. Epub 2022 Oct 10. J Exp Med. 2022. PMID: 36214813 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Eating away T cell responses in lung cancer.J Exp Med. 2022 Dec 5;219(12):e20221449. doi: 10.1084/jem.20221449. Epub 2022 Oct 10. J Exp Med. 2022. PMID: 36214813 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of DSTYK activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling and glycolysis in lung adenocarcinoma.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Dec 1;12(12):1122. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04385-1. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34853310 Free PMC article.
-
DSTYK Enhances Chemoresistance in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells.Cells. 2021 Dec 29;11(1):97. doi: 10.3390/cells11010097. Cells. 2021. PMID: 35011659 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of LKB1 Activity on the Sensitivity to PI3K/mTOR Inhibition in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2019 Jun;14(6):1061-1076. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2019.02.019. Epub 2019 Feb 27. J Thorac Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30825612 Free PMC article.
-
Dstyk mutation leads to congenital scoliosis-like vertebral malformations in zebrafish via dysregulated mTORC1/TFEB pathway.Nat Commun. 2020 Jan 24;11(1):479. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-14169-z. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 31980602 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Understanding the molecular regulatory mechanisms of autophagy in lung disease pathogenesis.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 31;15:1460023. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1460023. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39544928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer Cell-Intrinsic Alterations Associated with an Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment and Resistance to Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 6;15(12):3076. doi: 10.3390/cancers15123076. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37370686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel [89Zr]-anti-PD-1-PET-CT to assess response to PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in lung cancer.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 28;14:1272570. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1272570. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37841258 Free PMC article.
-
Trametinib sensitizes KRAS-mutant lung adenocarcinoma tumors to PD-1/PD-L1 axis blockade via Id1 downregulation.Mol Cancer. 2024 Apr 20;23(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-01991-3. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38643157 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Campbell, J.D., Alexandrov A., Kim J., Wala J., Berger A.H., Pedamallu C.S., Shukla S.A., Guo G., Brooks A.N., Murray B.A., et al. . 2016. Distinct patterns of somatic genome alterations in lung adenocarcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas. Nat. Genet. 48:607–616. 10.1038/ng.3564 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

