High-throughput small molecule screen identifies inhibitors of microsporidia invasion and proliferation in C. elegans
- PMID: 36163337
- PMCID: PMC9513054
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-33400-y
High-throughput small molecule screen identifies inhibitors of microsporidia invasion and proliferation in C. elegans
Abstract
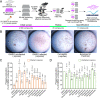
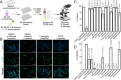
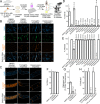
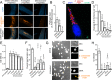
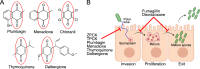
Microsporidia are a diverse group of fungal-related obligate intracellular parasites that infect most animal phyla. Despite the emerging threat that microsporidia represent to humans and agricultural animals, few reliable treatment options exist. Here, we develop a high-throughput screening method for the identification of chemical inhibitors of microsporidia infection, using liquid cultures of Caenorhabditis elegans infected with the microsporidia species Nematocida parisii. We screen a collection of 2560 FDA-approved compounds and natural products, and identify 11 candidate microsporidia inhibitors. Five compounds prevent microsporidia infection by inhibiting spore firing, whereas one compound, dexrazoxane, slows infection progression. The compounds have in vitro activity against several other microsporidia species, including those known to infect humans. Together, our results highlight the effectiveness of C. elegans as a model host for drug discovery against intracellular pathogens, and provide a scalable high-throughput system for the identification and characterization of microsporidia inhibitors.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Screening of the Pandemic Response Box identifies anti-microsporidia compounds.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023 Dec 8;17(12):e0011806. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0011806. eCollection 2023 Dec. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023. PMID: 38064503 Free PMC article.
-
A Large Collection of Novel Nematode-Infecting Microsporidia and Their Diverse Interactions with Caenorhabditis elegans and Other Related Nematodes.PLoS Pathog. 2016 Dec 12;12(12):e1006093. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006093. eCollection 2016 Dec. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27942022 Free PMC article.
-
Conservation of Nematocida microsporidia gene expression and host response in Caenorhabditis nematodes.PLoS One. 2022 Dec 19;17(12):e0279103. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0279103. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36534656 Free PMC article.
-
Host-Microsporidia Interactions in Caenorhabditis elegans, a Model Nematode Host.Microbiol Spectr. 2016 Oct;4(5). doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.FUNK-0003-2016. Microbiol Spectr. 2016. PMID: 27763260 Review.
-
Microsporidia: Pervasive natural pathogens of Caenorhabditis elegans and related nematodes.J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2024 Sep-Oct;71(5):e13027. doi: 10.1111/jeu.13027. Epub 2024 May 3. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38702921 Review.
Cited by
-
Screening of the Pandemic Response Box identifies anti-microsporidia compounds.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023 Dec 8;17(12):e0011806. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0011806. eCollection 2023 Dec. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023. PMID: 38064503 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput phenotyping of infection by diverse microsporidia species reveals a wild C. elegans strain with opposing resistance and susceptibility traits.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Mar 9;19(3):e1011225. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011225. eCollection 2023 Mar. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 36893187 Free PMC article.
-
An intestinally secreted host factor promotes microsporidia invasion of C. elegans.Elife. 2022 Jan 7;11:e72458. doi: 10.7554/eLife.72458. Elife. 2022. PMID: 34994689 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic and phenotypic evolution of nematode-infecting microsporidia.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Jul 20;19(7):e1011510. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011510. eCollection 2023 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 37471459 Free PMC article.
-
Bleomycin reduces Vairimorpha (Nosema) ceranae infection in honey bees with some evident host toxicity.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Feb 6;12(2):e0334923. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03349-23. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38179918 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

