LC-MS/MS Phytochemical Profiling, Antioxidant Activity, and Cytotoxicity of the Ethanolic Extract of Atriplex halimus L. against Breast Cancer Cell Lines: Computational Studies and Experimental Validation
- PMID: 36145377
- PMCID: PMC9503641
- DOI: 10.3390/ph15091156
LC-MS/MS Phytochemical Profiling, Antioxidant Activity, and Cytotoxicity of the Ethanolic Extract of Atriplex halimus L. against Breast Cancer Cell Lines: Computational Studies and Experimental Validation
Abstract
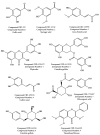
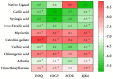
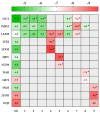
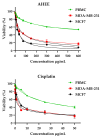
Atriplex halimus L., also known as Mediterranean saltbush, and locally as "Lgtef", an halophytic shrub, is used extensively to treat a wide variety of ailments in Morocco. The present study was undertaken to determine the antioxidant activity and cytotoxicity of the ethanolic extract of A. halimus leaves (AHEE). We first determined the phytochemical composition of AHEE using a liquid chromatography (LC)-tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) technique. The antioxidant activity was evaluated using different methods including DPPH scavenging capacity, β-carotene bleaching assay, ABTS scavenging, iron chelation, and the total antioxidant capacity assays. Cytotoxicity was investigated against human cancer breast cells lines MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231. The results showed that the components of the extract are composed of phenolic acids and flavonoids. The DPPH test showed strong scavenging capacity for the leaf extract (IC50 of 0.36 ± 0.05 mg/mL) in comparison to ascorbic acid (IC50 of 0.19 ± 0.02 mg/mL). The β-carotene test determined an IC50 of 2.91 ± 0.14 mg/mL. The IC50 values of ABTS, iron chelation, and TAC tests were 44.10 ± 2.92 TE µmol/mL, 27.40 ± 1.46 mg/mL, and 124 ± 1.27 µg AAE/mg, respectively. In vitro, the AHE extract showed significant inhibitory activity in all tested tumor cell lines, and the inhibition activity was found in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, computational techniques such as molecular docking and ADMET analysis were used in this work. Moreover, the physicochemical parameters related to the compounds' pharmacokinetic indicators were evaluated, including absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity prediction (Pro-Tox II).
Keywords: ADMET analysis; Atriplex halimus L.; antioxidant activity; breast cancer; computational study; cytotoxicity; toxicity prediction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chemical profiling of volatile compounds of the essential oil of grey-leaved rockrose (Cistus albidus L.) and its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antifungal, and anticancer activity in vitro and in silico.Front Chem. 2024 Feb 15;12:1334028. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1334028. eCollection 2024. Front Chem. 2024. PMID: 38435667 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Multi-Faceted Potential of Carob (Ceratonia siliqua var. Rahma) Leaves from Morocco: A Comprehensive Analysis of Polyphenols Profile, Antimicrobial Activity, Cytotoxicity against Breast Cancer Cell Lines, and Genotoxicity.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Jun 5;16(6):840. doi: 10.3390/ph16060840. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37375787 Free PMC article.
-
Protoscolicidal activity of Atriplex halimus leaves extract against Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces.Exp Parasitol. 2021 Oct;229:108155. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2021.108155. Epub 2021 Sep 2. Exp Parasitol. 2021. PMID: 34480915
-
Comparative study of the anthelmintic activity of ethanolic and aqueous extracts of Atriplex halimus, the anti-echinococcal plant used in Algeria.Vet Parasitol Reg Stud Reports. 2024 Sep;54:101094. doi: 10.1016/j.vprsr.2024.101094. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Vet Parasitol Reg Stud Reports. 2024. PMID: 39237235
-
Antioxidant activities and phytochemical constituents of Antidesma thwaitesianum Müll. Arg. leaf extracts.J Integr Med. 2017 Jul;15(4):310-319. doi: 10.1016/S2095-4964(17)60334-0. J Integr Med. 2017. PMID: 28659236
Cited by
-
Antiphotoaging and Skin-Protective Activities of Ardisia silvestris Ethanol Extract in Human Keratinocytes.Plants (Basel). 2023 Mar 3;12(5):1167. doi: 10.3390/plants12051167. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36904025 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity, Cytotoxicity, and Genotoxicity of Ptychotis verticillata Essential Oil: Towards Novel Breast Cancer Therapeutics.Life (Basel). 2023 Jul 19;13(7):1586. doi: 10.3390/life13071586. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37511960 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the multifaceted bioactivities of Lavandula pinnata L. essential oil: promising pharmacological activities.Front Chem. 2024 Apr 8;12:1383731. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1383731. eCollection 2024. Front Chem. 2024. PMID: 38660570 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical profiling of volatile compounds of the essential oil of grey-leaved rockrose (Cistus albidus L.) and its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antifungal, and anticancer activity in vitro and in silico.Front Chem. 2024 Feb 15;12:1334028. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1334028. eCollection 2024. Front Chem. 2024. PMID: 38435667 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological Properties of Chemically Characterized Extracts from Mastic Tree: In Vitro and In Silico Assays.Life (Basel). 2023 Jun 14;13(6):1393. doi: 10.3390/life13061393. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37374175 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Castagné R., Kelly-Irving M., Campanella G., Guida F., Krogh V., Palli D., Panico S., Sacerdote C., Tumino R., Kleinjans J. Biological Marks of Early-Life Socioeconomic Experience Is Detected in the Adult Inflammatory Transcriptome. Sci. Rep. 2016;6:38705. doi: 10.1038/srep38705. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

