P16INK4A-More Than a Senescence Marker
- PMID: 36143369
- PMCID: PMC9501954
- DOI: 10.3390/life12091332
P16INK4A-More Than a Senescence Marker
Abstract
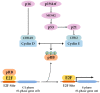
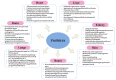
Aging is a biological feature that is characterized by gradual degeneration of function in cells, tissues, organs, or an intact organism due to the accumulation of environmental factors and stresses with time. Several factors have been attributed to aging such as oxidative stress and augmented production or exposure to reactive oxygen species, inflammatory cytokines production, telomere shortening, DNA damage, and, importantly, the deposit of senescent cells. These are irreversibly mitotically inactive, yet metabolically active cells. The reason underlying their senescence lies within the extrinsic and the intrinsic arms. The extrinsic arm is mainly characterized by the expression and the secretory profile known as the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP). The intrinsic arm results from the impact of several genes meant to regulate the cell cycle, such as tumor suppressor genes. P16INK4A is a tumor suppressor and cell cycle regulator that has been linked to aging and senescence. Extensive research has revealed that p16 expression is significantly increased in senescent cells, as well as during natural aging or age-related pathologies. Based on this fact, p16 is considered as a specific biomarker for detecting senescent cells and aging. Other studies have found that p16 is not only a senescence marker, but also a protein with many functions outside of senescence and aging. In this paper, we discuss and shed light on several studies that show the different functions of p16 and provide insights in its role in several biological processes besides senescence and aging.
Keywords: aging; cancer; development; p16; pathologies; senescence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tumor suppressor and aging biomarker p16(INK4a) induces cellular senescence without the associated inflammatory secretory phenotype.J Biol Chem. 2011 Oct 21;286(42):36396-403. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.257071. Epub 2011 Aug 31. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21880712 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular Senescence in Diabetes Mellitus: Distinct Senotherapeutic Strategies for Adipose Tissue and Pancreatic β Cells.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 31;13:869414. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.869414. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35432205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Senescent Cells in the Bone Microenvironment.J Bone Miner Res. 2016 Nov;31(11):1920-1929. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2892. Epub 2016 Oct 24. J Bone Miner Res. 2016. PMID: 27341653 Free PMC article.
-
p16Ink4a deletion in cells of the intervertebral disc affects their matrix homeostasis and senescence associated secretory phenotype without altering onset of senescence.Matrix Biol. 2019 Sep;82:54-70. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2019.02.004. Epub 2019 Feb 24. Matrix Biol. 2019. PMID: 30811968 Free PMC article.
-
Senescence in Health and Disease.Cell. 2017 Jun 1;169(6):1000-1011. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.015. Cell. 2017. PMID: 28575665 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In Vitro Osteogenesis Study of Shell Nacre Cement with Older and Young Donor Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Jan 31;11(2):143. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11020143. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38391629 Free PMC article.
-
p16 Expression in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Surrogate or Independent Prognostic Marker?Pathogens. 2024 Jan 24;13(2):100. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13020100. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 38392838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Senescence of alveolar epithelial progenitor cells: a critical driver of lung fibrosis.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2023 Aug 1;325(2):C483-C495. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00239.2023. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37458437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PR55α-controlled protein phosphatase 2A inhibits p16 expression and blocks cellular senescence induction by γ-irradiation.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Mar 4;16(5):4116-4137. doi: 10.18632/aging.205619. Epub 2024 Mar 4. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38441530 Free PMC article.
-
Senotherapeutics to Counteract Senescent Cells Are Prominent Topics in the Context of Anti-Ageing Strategies.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 1;25(3):1792. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031792. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38339070 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stone S., Jiang P., Dayananth P., Tavtigian S.V., Katcher H., Parry D., Peters G., Kamb A. Complex structure and regulation of the P16 (MTS1) locus. Cancer Res. 1995;55:2988–2994. - PubMed
-
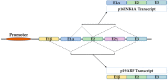
- Mao L., Merlo A., Bedi G., Shapiro G.I., Edwards C.D., Rollins B.J., Sidransky D. A novel p16INK4A transcript. Cancer Res. 1995;55:2995–2997. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

