Ultrasonic-Assisted Synthesis of Benzofuran Appended Oxadiazole Molecules as Tyrosinase Inhibitors: Mechanistic Approach through Enzyme Inhibition, Molecular Docking, Chemoinformatics, ADMET and Drug-Likeness Studies
- PMID: 36142889
- PMCID: PMC9500974
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231810979
Ultrasonic-Assisted Synthesis of Benzofuran Appended Oxadiazole Molecules as Tyrosinase Inhibitors: Mechanistic Approach through Enzyme Inhibition, Molecular Docking, Chemoinformatics, ADMET and Drug-Likeness Studies
Abstract
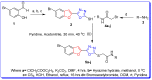
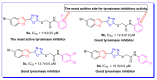
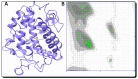
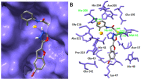
Furan-oxadiazole structural hybrids belong to the most promising and biologically active classes of oxygen and nitrogen containing five member heterocycles which have expanded therapeutic scope and potential in the fields of pharmacology, medicinal chemistry and pharmaceutics. A novel series 5a-j of benzofuran-oxadiazole molecules incorporating S-alkylated amide linkage have been synthesized using ultrasonic irradiation and screened for bacterial tyrosinase inhibition activity. Most of the synthesized furan-oxadiazole structural motifs exhibited significant tyrosinase inhibition activity in the micromolar range, with one of the derivatives being more potent than the standard drug ascorbic acid. Among the tested compounds, the scaffold 5a displayed more tyrosinase inhibition efficacy IC50 (11 ± 0.25 μM) than the ascorbic acid IC50 (11.5 ± 0.1 μM). Compounds 5b, 5c and 5d efficiently inhibited bacterial tyrosinase with IC50 values in the range of 12.4 ± 0.0-15.5 ± 0.0 μM. The 2-fluorophenylacetamide containing furan-oxadiazole compound 5a may be considered as a potential lead for tyrosinase inhibition with lesser side effects as a skin whitening and malignant melanoma anticancer agent.
Keywords: ADMET study; chemoinformatics; furan-oxadiazole molecules; molecular docking; structure-activity relationship; tyrosinase inhibitors; ultrasonic-assisted green synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel Amide Derivatives as Potent Tyrosinase Inhibitors; In-vitro, In-vivo Antimelanogenic Activity and Computational Studies.Med Chem. 2019;15(7):715-728. doi: 10.2174/1573406415666190319101329. Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30892163
-
Synthesis, computational studies, tyrosinase inhibitory kinetics and antimelanogenic activity of hydroxy substituted 2-[(4-acetylphenyl)amino]-2-oxoethyl derivatives.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2019 Dec;34(1):1-11. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2019.1654468. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31456445 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound mediated efficient synthesis of new 4-oxoquinazolin-3(4H)-yl)furan-2-carboxamides as potent tyrosinase inhibitors: Mechanistic approach through chemoinformatics and molecular docking studies.Bioorg Chem. 2019 Nov;92:103201. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.103201. Epub 2019 Aug 13. Bioorg Chem. 2019. PMID: 31445195
-
Research progress on the synthesis and pharmacology of 1,3,4-oxadiazole and 1,2,4-oxadiazole derivatives: a mini review.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022 Dec;37(1):2304-2319. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2115036. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36000176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
1,3,4-Oxadiazole Scaffold in Antidiabetic Drug Discovery: An Overview.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024;24(20):1800-1821. doi: 10.2174/0113895575298181240410041029. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38644715 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of novel 1,2,4-triazole tethered β-hydroxy sulfides as bacterial tyrosinase inhibitors: synthesis and biophysical evaluation through in vitro and in silico approaches.RSC Adv. 2024 May 13;14(22):15419-15430. doi: 10.1039/d4ra01252f. eCollection 2024 May 10. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38741974 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Biomedical Potential and Molecular Docking Analyses of Coumarin-Triazole Hybrids as Tyrosinase Inhibitors: Design, Synthesis, In Vitro Profiling, and In Silico Studies.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Apr 20;17(4):532. doi: 10.3390/ph17040532. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38675492 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Review on Benzofuran Synthesis Featuring Innovative and Catalytic Strategies.ACS Omega. 2024 May 6;9(19):20728-20752. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c02677. eCollection 2024 May 14. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38764672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Silico Development of Novel Benzofuran-1,3,4-Oxadiazoles as Lead Inhibitors of M. tuberculosis Polyketide Synthase 13.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Jun 1;16(6):829. doi: 10.3390/ph16060829. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37375776 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Synthetic Chemistry of Phenyl-3-(5-aryl-2-furyl)- 2-propen-1-ones as Urease Inhibitors: Mechanistic Approach through Urease Inhibition, Molecular Docking and Structure-Activity Relationship.Biomedicines. 2023 Aug 30;11(9):2428. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11092428. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37760869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nazir Y., Saeed A., Rafiq M., Afzal S., Ali A., Latif M., Zuegg J., Hussein W.M., Fercher C., Barnard R.T., et al. Hydroxyl substituted benzoic acid/cinnamic acid derivatives: Tyrosinase inhibitory kinetics, anti-melanogenic activity and molecular docking studies. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019;30:126722. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2019.126722. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Collins R.P., Warner L.B., Paige L. The Tyrosinase Activity of StrobilomycesStrobilaceus. Mycologia. 1963;55:764–774. doi: 10.1080/00275514.1963.12018067. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

