Highly Bright Silica-Coated InP/ZnS Quantum Dot-Embedded Silica Nanoparticles as Biocompatible Nanoprobes
- PMID: 36142888
- PMCID: PMC9502493
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231810977
Highly Bright Silica-Coated InP/ZnS Quantum Dot-Embedded Silica Nanoparticles as Biocompatible Nanoprobes
Abstract
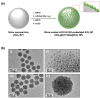
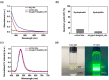
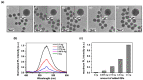
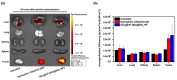
Quantum dots (QDs) have outstanding optical properties such as strong fluorescence, excellent photostability, broad absorption spectra, and narrow emission bands, which make them useful for bioimaging. However, cadmium (Cd)-based QDs, which have been widely studied, have potential toxicity problems. Cd-free QDs have also been studied, but their weak photoluminescence (PL) intensity makes their practical use in bioimaging challenging. In this study, Cd-free QD nanoprobes for bioimaging were fabricated by densely embedding multiple indium phosphide/zinc sulfide (InP/ZnS) QDs onto silica templates and coating them with a silica shell. The fabricated silica-coated InP/ZnS QD-embedded silica nanoparticles (SiO2@InP QDs@SiO2 NPs) exhibited hydrophilic properties because of the surface silica shell. The quantum yield (QY), maximum emission peak wavelength, and full-width half-maximum (FWHM) of the final fabricated SiO2@InP QDs@SiO2 NPs were 6.61%, 527.01 nm, and 44.62 nm, respectively. Moreover, the brightness of the particles could be easily controlled by adjusting the amount of InP/ZnS QDs in the SiO2@InP QDs@SiO2 NPs. When SiO2@InP QDs@SiO2 NPs were administered to tumor syngeneic mice, the fluorescence signal was prominently detected in the tumor because of the preferential distribution of the SiO2@InP QDs@SiO2 NPs, demonstrating their applicability in bioimaging with NPs. Thus, SiO2@InP QDs@SiO2 NPs have the potential to successfully replace Cd-based QDs as highly bright and biocompatible fluorescent nanoprobes.
Keywords: biocompatible nanoprobes; bioimaging; in vivo; photoluminescence (PL); quantum dots (QDs); silica-coated InP/ZnS QD-embedded silica nanoparticles; syngeneic mice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sensitive Immunoassay Based on Biocompatible and Robust Silica-Coated Cd-Free InP-Based Quantum Dots.Inorg Chem. 2021 May 3;60(9):6503-6513. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.1c00304. Epub 2021 Apr 13. Inorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 33847486
-
Synthesis and Degradation of Cadmium-Free InP and InPZn/ZnS Quantum Dots in Solution.Langmuir. 2018 Nov 20;34(46):13924-13934. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b02402. Epub 2018 Nov 6. Langmuir. 2018. PMID: 30351964 Free PMC article.
-
Extending the Near-Infrared Emission Range of Indium Phosphide Quantum Dots for Multiplexed In Vivo Imaging.Nano Lett. 2021 Apr 14;21(7):3271-3279. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c00600. Epub 2021 Mar 23. Nano Lett. 2021. PMID: 33755481 Free PMC article.
-
Luminescent quantum dots: Synthesis, optical properties, bioimaging and toxicity.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2023 Jun;197:114830. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2023.114830. Epub 2023 Apr 20. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2023. PMID: 37086917 Review.
-
Synthesis and Application of Silica-Coated Quantum Dots in Biomedicine.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 18;22(18):10116. doi: 10.3390/ijms221810116. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34576279 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advanced Optical Materials: From Materials to Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 31;24(21):15790. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115790. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958773 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Tracking of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Using Ultra-Sensitive Quantum Dot-Embedded Silica Nanoparticles.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 17;24(6):5794. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065794. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982869 Free PMC article.
-
Silica Encapsulation of Hydrophobic Optical NP-Embedded Silica Particles with Trimethoxy(2-Phenylethyl)silane.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Jul 24;13(14):2145. doi: 10.3390/nano13142145. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37513156 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Optical Nano/Micromaterials.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 18;24(8):7458. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087458. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108618 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Breakthroughs in Using Quantum Dots for Cancer Imaging and Drug Delivery Purposes.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Sep 15;13(18):2566. doi: 10.3390/nano13182566. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37764594 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dabbousi B.O., Rodriguez-Viejo J., Mikulec F.V., Heine J.R., Mattoussi H., Ober R., Jensen K.F., Bawendi M.G. (CdSe) ZnS core–shell quantum dots: Synthesis and characterization of a size series of highly luminescent nanocrystallites. J. Phys. Chem. B. 1997;101:9463–9475. doi: 10.1021/jp971091y. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

