Formation Mechanism of Inter-Crosslink in DNA by Nitrogen Oxides Pollutants through A Diazonium Intermediate
- PMID: 36142522
- PMCID: PMC9502170
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231810621
Formation Mechanism of Inter-Crosslink in DNA by Nitrogen Oxides Pollutants through A Diazonium Intermediate
Abstract
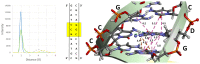
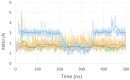
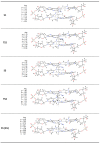
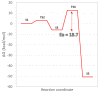
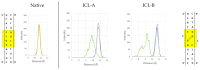
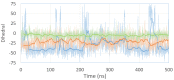
Outdoor air pollution is a mixture of multiple atmospheric pollutants, among which nitrogen oxide (NOx) stands out due to its association with several diseases. NOx reactivity can conduct to DNA damage as severe as interstrand crosslinks (ICL) formation, that in turn is able to block DNA replication and transcription. Experimental studies have suggested that the ICL formation due to NOx is realized through a diazonium intermediate (DI). In this work, we have modeled the DI structure, including a DNA double-strand composed of two base pairs GC/CG, being diazotized as one of the guanine nucleotides. The structural stability of DNA with DI lesion was essayed through 500 ns molecular dynamics simulations. It was found that the DNA structure of the oligonucleotide is stable when the DI is present since the loss of a Guanine-Cytosine hydrogen bond is replaced by the presence of two cation-π interactions. Additionally, we have studied the mechanism of formation of a crosslink between the two guanine nucleobases from the modeled DI by carrying out DFT calculations at the M06-L/DNP+ level of theory. Our results show that the mechanism is thermodynamically favored by a strong stabilization of the ICL product, and the process is kinetically viable since its limiting stage is accessible.
Keywords: DFT; DNA; MD; inter-crosslink; nitrogen oxide; pollutant.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structural dynamics and cation interactions of DNA quadruplex molecules containing mixed guanine/cytosine quartets revealed by large-scale MD simulations.J Am Chem Soc. 2001 Apr 11;123(14):3295-307. doi: 10.1021/ja002656y. J Am Chem Soc. 2001. PMID: 11457065
-
Refinement of DNA structures through near-edge X-ray absorption fine structure analysis: applications on guanine and cytosine nucleobases, nucleosides, and nucleotides.J Phys Chem B. 2010 Oct 21;114(41):13214-22. doi: 10.1021/jp1034745. J Phys Chem B. 2010. PMID: 20873844
-
Chasing Particularities of Guanine- and Cytosine-Rich DNA Strands.Molecules. 2020 Jan 21;25(3):434. doi: 10.3390/molecules25030434. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 31972988 Free PMC article.
-
DNA triple helix formation at target sites containing several pyrimidine interruptions: stabilization by protonated cytosine or 5-(1-propargylamino)dU.Biochemistry. 1999 Oct 12;38(41):13747-58. doi: 10.1021/bi9911637. Biochemistry. 1999. PMID: 10521282
-
The Two Faces of the Guanyl Radical: Molecular Context and Behavior.Molecules. 2021 Jun 9;26(12):3511. doi: 10.3390/molecules26123511. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34207639 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Air Pollution on the Basal DNA Damage of Mother-Newborn Couples of México City.Toxics. 2023 Sep 9;11(9):766. doi: 10.3390/toxics11090766. Toxics. 2023. PMID: 37755776 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balakrishnan K., Chen G., Brauer M., Chow J., DeMarini D.M., Knudsen L.E., Forastiere F., Laden F., Heinrich U., Morgan D.L., et al. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Outdoor Air Pollution. Volume 109. International Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon, France: 2015.
-
- Air Quality in Europe–2021 Report. European Environment Agency; Copenhagen, Denmark: 2021. EEA report No. 15/2021. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

