Micro-Players of Great Significance-Host microRNA Signature in Viral Infections in Humans and Animals
- PMID: 36142450
- PMCID: PMC9504570
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231810536
Micro-Players of Great Significance-Host microRNA Signature in Viral Infections in Humans and Animals
Abstract
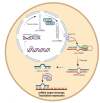
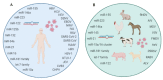
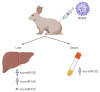
Over time, more and more is becoming known about micro-players of great significance. This is particularly the case for microRNAs (miRNAs; miR), which have been found to participate in the regulation of many physiological and pathological processes in both humans and animals. One such process is viral infection in humans and animals, in which the host miRNAs-alone or in conjunction with the virus-interact on two levels: viruses may regulate the host's miRNAs to evade its immune system, while the host miRNAs can play anti- or pro-viral roles. The purpose of this comprehensive review is to present the key miRNAs involved in viral infections in humans and animals. We summarize the data in the available literature, indicating that the signature miRNAs in human viral infections mainly include 12 miRNAs (i.e., miR-155, miR-223, miR-146a, miR-122, miR-125b, miR-132, miR-34a, miR -21, miR-16, miR-181 family, let-7 family, and miR-10a), while 10 miRNAs are commonly found in animals (i.e., miR-155, miR-223, miR-146a, miR-145, miR-21, miR-15a/miR-16 cluster, miR-181 family, let-7 family, and miR-122) in this context. Knowledge of which miRNAs are involved in different viral infections and the biological functions that they play can help in understanding the pathogenesis of viral diseases, facilitating the future development of therapeutic agents for both humans and animals.
Keywords: Lagovirus europaeus/RHDV; Marek’s disease virus; foot-and-mouth disease virus; hemorrhagic viruses; hepatitis viruses; microRNA; porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus; rabies virus; respiratory viruses; viral infections.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Digital PCR (dPCR) Quantification of miR-155-5p as a Potential Candidate for a Tissue Biomarker of Inflammation in Rabbits Infected with Lagovirus europaeus/Rabbit Hemorrhagic Disease Virus (RHDV).Viruses. 2023 Jul 19;15(7):1578. doi: 10.3390/v15071578. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37515264 Free PMC article.
-
Host Cells Actively Resist Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Infection via the IRF8-MicroRNA-10a-SRP14 Regulatory Pathway.J Virol. 2022 Apr 13;96(7):e0000322. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00003-22. Epub 2022 Mar 16. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35293774 Free PMC article.
-
Role of virus-encoded microRNAs in Avian viral diseases.Viruses. 2014 Mar 21;6(3):1379-94. doi: 10.3390/v6031379. Viruses. 2014. PMID: 24662606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-376b-3p Promotes Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Replication by Targeting Viral Restriction Factor TRIM22.J Virol. 2022 Jan 26;96(2):e0159721. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01597-21. Epub 2021 Nov 10. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 34757838 Free PMC article.
-
Virus-Derived Small RNAs and microRNAs in Health and Disease.Annu Rev Biomed Data Sci. 2023 Aug 10;6:275-298. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biodatasci-122220-111429. Epub 2023 May 9. Annu Rev Biomed Data Sci. 2023. PMID: 37159873 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs Regulate the Expression of Genes Related to the Innate Immune and Inflammatory Response in Rabbits Infected with Lagovirus europaeus GI.1 and GI.2 Genotypes.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 2;25(17):9531. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179531. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273479 Free PMC article.
-
The hidden RNA code: implications of the RNA epitranscriptome in the context of viral infections.Front Genet. 2023 Aug 1;14:1245683. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1245683. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37614818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of miR-29a as a novel biomarker for lumpy skin disease virus exposure in cattle.Virulence. 2024 Dec;15(1):2324711. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2024.2324711. Epub 2024 Mar 25. Virulence. 2024. PMID: 38527940 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B Virus and microRNAs: A Bioinformatics Approach.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 7;24(24):17224. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417224. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating and extracellular vesicle-derived microRNAs as biomarkers in bone-related diseases.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 May 24;14:1168898. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1168898. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37293498 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

