Identifying Drug Targets of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma through a Systems Biology Method and Genome-Wide Microarray Data for Drug Discovery by Deep Learning and Drug Design Specifications
- PMID: 36142321
- PMCID: PMC9499358
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231810409
Identifying Drug Targets of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma through a Systems Biology Method and Genome-Wide Microarray Data for Drug Discovery by Deep Learning and Drug Design Specifications
Abstract
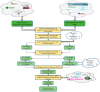
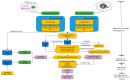
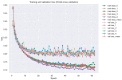
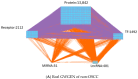
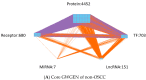
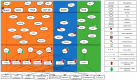
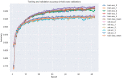
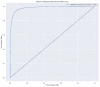
In this study, we provide a systems biology method to investigate the carcinogenic mechanism of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) in order to identify some important biomarkers as drug targets. Further, a systematic drug discovery method with a deep neural network (DNN)-based drug-target interaction (DTI) model and drug design specifications is proposed to design a potential multiple-molecule drug for the medical treatment of OSCC before clinical trials. First, we use big database mining to construct the candidate genome-wide genetic and epigenetic network (GWGEN) including a protein-protein interaction network (PPIN) and a gene regulatory network (GRN) for OSCC and non-OSCC. In the next step, real GWGENs are identified for OSCC and non-OSCC by system identification and system order detection methods based on the OSCC and non-OSCC microarray data, respectively. Then, the principal network projection (PNP) method was used to extract core GWGENs of OSCC and non-OSCC from real GWGENs of OSCC and non-OSCC, respectively. Afterward, core signaling pathways were constructed through the annotation of KEGG pathways, and then the carcinogenic mechanism of OSCC was investigated by comparing the core signal pathways and their downstream abnormal cellular functions of OSCC and non-OSCC. Consequently, HES1, TCF, NF-κB and SP1 are identified as significant biomarkers of OSCC. In order to discover multiple molecular drugs for these significant biomarkers (drug targets) of the carcinogenic mechanism of OSCC, we trained a DNN-based drug-target interaction (DTI) model by DTI databases to predict candidate drugs for these significant biomarkers. Finally, drug design specifications such as adequate drug regulation ability, low toxicity and high sensitivity are employed to filter out the appropriate molecular drugs metformin, gefitinib and gallic-acid to combine as a potential multiple-molecule drug for the therapeutic treatment of OSCC.
Keywords: deep neural network-based drug–target interaction (DNN-based DTI) model; drug design specifications; genome-wide genetic and epigenetic network (GWGEN); oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC); significant biomarkers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Systems Drug Design for Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer and Advanced Bladder Cancer by Genome-Wide Microarray Data and Deep Learning Method with Drug Design Specifications.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 10;23(22):13869. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213869. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430344 Free PMC article.
-
Systems Approach to Pathogenic Mechanism of Type 2 Diabetes and Drug Discovery Design Based on Deep Learning and Drug Design Specifications.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 26;22(1):166. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010166. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33375269 Free PMC article.
-
Drug Target Identification and Drug Repurposing in Psoriasis through Systems Biology Approach, DNN-Based DTI Model and Genome-Wide Microarray Data.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 12;24(12):10033. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210033. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373186 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress of Metformin in the Treatment of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Endocrinology. 2023 Sep 23;164(11):bqad139. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqad139. Endocrinology. 2023. PMID: 37738154 Review.
-
Translational genomics and recent advances in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Semin Cancer Biol. 2020 Apr;61:71-83. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.09.011. Epub 2019 Sep 19. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020. PMID: 31542510 Review.
Cited by
-
Panoramic view of key cross-talks underpinning the oral squamous cell carcinoma stemness - unearthing the future opportunities.Front Oncol. 2023 Dec 19;13:1247399. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1247399. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38170015 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Da Silva S.D., Marchi F.A., Xu B., Bijian K., Alobaid F., Mlynarek A., Rogatto S.R., Hier M., Kowalski L.P., Alaoui-Jamali M.A. Predominant Rab-GTPase amplicons contributing to oral squamous cell carcinoma progression to metastasis. Oncotarget. 2015;6:21950. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4277. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

