Hemodynamics and Tissue Optical Properties in Bimodal Infarctions Induced by Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion
- PMID: 36142225
- PMCID: PMC9499323
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms231810318
Hemodynamics and Tissue Optical Properties in Bimodal Infarctions Induced by Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion
Abstract
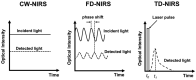
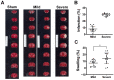
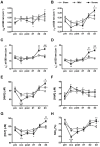
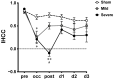
Various infarct sizes induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) generate inconsistent outcomes for stroke preclinical study. Monitoring cerebral hemodynamics may help to verify the outcome of MCAO. The aim of this study was to investigate the changes in brain tissue optical properties by frequency-domain near-infrared spectroscopy (FD-NIRS), and establish the relationship between cerebral hemodynamics and infarct variation in MCAO model. The rats were undergone transient MCAO using intraluminal filament. The optical properties and hemodynamics were measured by placing the FD-NIRS probes on the scalp of the head before, during, and at various time-courses after MCAO. Bimodal infarction severities were observed after the same 90-min MCAO condition. Significant decreases in concentrations of oxygenated hemoglobin ([HbO]) and total hemoglobin ([HbT]), tissue oxygenation saturation (StO2), absorption coefficient (μa) at 830 nm, and reduced scattering coefficient (μs') at both 690 and 830 nm were detected during the occlusion in the severe infarction but not the mild one. Of note, the significant increases in [HbO], [HbT], StO2, and μa at both 690 and 830 nm were found on day 3; and increases in μs' at both 690 and 830 nm were found on day 2 and day 3 after MCAO, respectively. The interhemispheric correlation coefficient (IHCC) was computed from low-frequency hemodynamic oscillation of both hemispheres. Lower IHCCs standing for interhemispheric desynchronizations were found in both mild and severe infarction during occlusion, and only in severe infarction after reperfusion. Our finding supports that sequential FD-NIRS parameters may associated with the severity of the infarction in MCAO model, and the consequent pathologies such as vascular dysfunction and brain edema. Further study is required to validate the potential use of FD-NIRS as a monitor for MCAO verification.
Keywords: absorption; cerebral blood flow; cerebral hemodynamics; interhemispheric correlation coefficient; ischemic stroke; middle cerebral artery occlusion; near infrared spectroscopy; scattering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interleaved imaging of cerebral hemodynamics and blood flow index to monitor ischemic stroke and treatment in rat by volumetric diffuse optical tomography.Neuroimage. 2014 Jan 15;85 Pt 1(0 1):566-82. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.07.020. Epub 2013 Jul 16. Neuroimage. 2014. PMID: 23872158 Free PMC article.
-
Near infrared spectroscopy detection of hemispheric cerebral ischemia following middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats.Neurochem Int. 2023 Jan;162:105460. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2022.105460. Epub 2022 Nov 28. Neurochem Int. 2023. PMID: 36455748 Free PMC article.
-
Noninvasive monitoring of estrogen effects against ischemic stroke in rats by near-infrared spectroscopy.Appl Opt. 2007 Dec 1;46(34):8315-21. doi: 10.1364/ao.46.008315. Appl Opt. 2007. PMID: 18059674
-
Modeling Transient Focal Ischemic Stroke in Rodents by Intraluminal Filament Method of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1717:101-113. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7526-6_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29468587 Review.
-
Evaluation of MCAO stroke models in normotensive rats: standardized neocortical infarction by the 3VO technique.Exp Neurol. 2003 Aug;182(2):261-74. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4886(03)00116-x. Exp Neurol. 2003. PMID: 12895438 Review.
Cited by
-
Distinct Alterations in Oxygenation, Ion Composition and Acid-Base Balance in Cerebral Collaterals During Large-Vessel Occlusion Stroke.Clin Neuroradiol. 2023 Dec;33(4):973-984. doi: 10.1007/s00062-023-01296-w. Epub 2023 Jun 7. Clin Neuroradiol. 2023. PMID: 37284875 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture protective effects after cerebral ischemia are mediated through miR-219a inhibition.Biol Res. 2023 Jun 30;56(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s40659-023-00448-z. Biol Res. 2023. PMID: 37391839 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benjamin E.J., Blaha M.J., Chiuve S.E., Cushman M., Das S.R., Deo R., de Ferranti S.D., Floyd J., Fornage M., Gillespie C., et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2017 update: A report from the american heart association. Circulation. 2017;135:e146–e603. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000485. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Navarro-Orozco D., Sánchez-Manso J.C. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing LLC.; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2022. Neuroanatomy, Middle Cerebral Artery. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- EX103-10139EI/National Health Research Institutes in Taiwan
- 104-2314-B-006-007-MY3, 101-2221-E-006-006-MY3, 110-2314-B-038-001, 110-2811-E-038-500-MY3, 110-2314-B-305-001, 109-2314-B-305-001, 109-2221-E-305-001-MY2, 109-2221-E-038-005-MY3, and 109-2314-B-038-132./Ministry of Science and Technology in Taiwan
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

