The Impact of Oxidative Stress and AKT Pathway on Cancer Cell Functions and Its Application to Natural Products
- PMID: 36139919
- PMCID: PMC9495789
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox11091845
The Impact of Oxidative Stress and AKT Pathway on Cancer Cell Functions and Its Application to Natural Products
Abstract
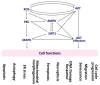
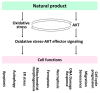
Oxidative stress and AKT serine-threonine kinase (AKT) are responsible for regulating several cell functions of cancer cells. Several natural products modulate both oxidative stress and AKT for anticancer effects. However, the impact of natural product-modulating oxidative stress and AKT on cell functions lacks systemic understanding. Notably, the contribution of regulating cell functions by AKT downstream effectors is not yet well integrated. This review explores the role of oxidative stress and AKT pathway (AKT/AKT effectors) on ten cell functions, including apoptosis, autophagy, endoplasmic reticulum stress, mitochondrial morphogenesis, ferroptosis, necroptosis, DNA damage response, senescence, migration, and cell-cycle progression. The impact of oxidative stress and AKT are connected to these cell functions through cell function mediators. Moreover, the AKT effectors related to cell functions are integrated. Based on this rationale, natural products with the modulating abilities for oxidative stress and AKT pathway exhibit the potential to regulate these cell functions, but some were rarely reported, particularly for AKT effectors. This review sheds light on understanding the roles of oxidative stress and AKT pathway in regulating cell functions, providing future directions for natural products in cancer treatment.
Keywords: AKT signaling; cell function; natural product; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest among them.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long Noncoding RNAs and Circular RNAs Regulate AKT and Its Effectors to Control Cell Functions of Cancer Cells.Cells. 2022 Sep 20;11(19):2940. doi: 10.3390/cells11192940. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36230902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impacts of Oxidative Stress and PI3K/AKT/mTOR on Metabolism and the Future Direction of Investigating Fucoidan-Modulated Metabolism.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 May 6;11(5):911. doi: 10.3390/antiox11050911. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35624775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of AKT Pathway-Targeting miRNAs for Cancer Cell Treatment with Natural Products.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 12;24(4):3688. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043688. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The (+)-Brevipolide H Displays Anticancer Activity against Human Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: The Role of Oxidative Stress and Akt/mTOR/p70S6K-Dependent Pathways in G1 Checkpoint Arrest and Apoptosis.Molecules. 2020 Jun 25;25(12):2929. doi: 10.3390/molecules25122929. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32630532 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress and AKT-Associated Angiogenesis in a Zebrafish Model and Its Potential Application for Withanolides.Cells. 2022 Mar 11;11(6):961. doi: 10.3390/cells11060961. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35326412 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Essential Oil from Conyza bonariensis (L.) Cronquist (Asteraceae) Exerts an In Vitro Antimelanoma Effect by Inducing Apoptosis and Modulating the MAPKs, NF-κB, and PKB/AKT Signaling Pathways.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Nov 2;16(11):1553. doi: 10.3390/ph16111553. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38004419 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the sequential changes of monocytes/macrophages in the progression of IDD with longitudinal approach using single-cell transcriptome.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 1;14:1090637. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1090637. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36817437 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Spicatoside a on Anti-Osteosarcoma MG63 Cells through Reactive Oxygen Species Generation and the Inhibition of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR Pathway.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Sep 25;13(10):1162. doi: 10.3390/antiox13101162. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456416 Free PMC article.
-
Prospects of compounds of herbal plants as anticancer agents: a comprehensive review from molecular pathways.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 22;15:1387866. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1387866. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39104398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Excavatolide C/cisplatin combination induces antiproliferation and drives apoptosis and DNA damage in bladder cancer cells.Arch Toxicol. 2024 May;98(5):1543-1560. doi: 10.1007/s00204-024-03699-1. Epub 2024 Feb 29. Arch Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38424264
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

