An ACE2-dependent Sarbecovirus in Russian bats is resistant to SARS-CoV-2 vaccines
- PMID: 36136995
- PMCID: PMC9498966
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010828
An ACE2-dependent Sarbecovirus in Russian bats is resistant to SARS-CoV-2 vaccines
Abstract
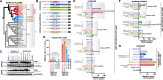
Spillover of sarbecoviruses from animals to humans has resulted in outbreaks of severe acute respiratory syndrome SARS-CoVs and the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. Efforts to identify the origins of SARS-CoV-1 and -2 has resulted in the discovery of numerous animal sarbecoviruses-the majority of which are only distantly related to known human pathogens and do not infect human cells. The receptor binding domain (RBD) on sarbecoviruses engages receptor molecules on the host cell and mediates cell invasion. Here, we tested the receptor tropism and serological cross reactivity for RBDs from two sarbecoviruses found in Russian horseshoe bats. While these two viruses are in a viral lineage distinct from SARS-CoV-1 and -2, the RBD from one virus, Khosta 2, was capable of using human ACE2 to facilitate cell entry. Viral pseudotypes with a recombinant, SARS-CoV-2 spike encoding for the Khosta 2 RBD were resistant to both SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies and serum from individuals vaccinated for SARS-CoV-2. Our findings further demonstrate that sarbecoviruses circulating in wildlife outside of Asia also pose a threat to global health and ongoing vaccine campaigns against SARS-CoV-2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Shows Cross-Protection against Bat SARS-Related Coronaviruses in Human ACE2 Transgenic Mice.J Virol. 2022 Apr 27;96(8):e0016922. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00169-22. Epub 2022 Mar 28. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35343762 Free PMC article.
-
Design of a bifunctional pan-sarbecovirus entry inhibitor targeting the cell receptor and viral fusion protein.J Virol. 2023 Aug 31;97(8):e0019223. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00192-23. Epub 2023 Aug 14. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 37578234 Free PMC article.
-
Broad receptor tropism and immunogenicity of a clade 3 sarbecovirus.Cell Host Microbe. 2023 Dec 13;31(12):1961-1973.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2023.10.018. Epub 2023 Nov 20. Cell Host Microbe. 2023. PMID: 37989312
-
Development of variant-proof severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, pan-sarbecovirus, and pan-β-coronavirus vaccines.J Med Virol. 2023 Jan;95(1):e28172. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28172. Epub 2022 Oct 6. J Med Virol. 2023. PMID: 36161303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perspectives on development of vaccines against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2020 Oct 2;16(10):2366-2369. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2020.1787064. Epub 2020 Sep 22. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2020. PMID: 32961082 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Broad cross neutralizing antibodies against sarbecoviruses generated by SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination in humans.NPJ Vaccines. 2024 Oct 22;9(1):195. doi: 10.1038/s41541-024-00997-8. NPJ Vaccines. 2024. PMID: 39438493 Free PMC article.
-
Sarbecovirus RBD indels and specific residues dictating multi-species ACE2 adaptiveness.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 14;15(1):8869. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53029-3. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39402048 Free PMC article.
-
Mosaic sarbecovirus nanoparticles elicit cross-reactive responses in pre-vaccinated animals.Cell. 2024 Oct 3;187(20):5554-5571.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.07.052. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Cell. 2024. PMID: 39197450 Free PMC article.
-
Structural characteristics of BtKY72 RBD bound to bat ACE2 reveal multiple key residues affecting ACE2 usage of sarbecoviruses.mBio. 2024 Sep 11;15(9):e0140424. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01404-24. Epub 2024 Jul 31. mBio. 2024. PMID: 39082798 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2-related bat viruses evade human intrinsic immunity but lack efficient transmission capacity.Nat Microbiol. 2024 Aug;9(8):2038-2050. doi: 10.1038/s41564-024-01765-z. Epub 2024 Jul 29. Nat Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39075235
References
-
- Hu B, Zeng LP, Yang XL, Ge XY, Zhang W, Li B, et al.. Discovery of a rich gene pool of bat SARS-related coronaviruses provides new insights into the origin of SARS coronavirus. PLoS Pathog. 2017;13(11):e1006698. Epub 2017/12/01. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006698 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC5708621. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Starr TN, Greaney AJ, Hilton SK, Ellis D, Crawford KHD, Dingens AS, et al.. Deep Mutational Scanning of SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Binding Domain Reveals Constraints on Folding and ACE2 Binding. Cell. 2020;182(5):1295–310 e20. Epub 2020/08/26. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.012 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC7418704. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou H, Ji J, Chen X, Bi Y, Li J, Wang Q, et al.. Identification of novel bat coronaviruses sheds light on the evolutionary origins of SARS-CoV-2 and related viruses. Cell. 2021;184(17):4380–91 e14. Epub 2021/06/21. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.06.008 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC8188299. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

