Localized PD-1 Blockade in a Mouse Model of Renal Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 36132332
- PMCID: PMC9486680
- DOI: 10.3389/fddev.2022.838458
Localized PD-1 Blockade in a Mouse Model of Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
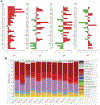
Herein we report the impact of localized delivery of an anti-mouse PD-1-specific monoclonal antibody (aPD1) on Renca tumors in the resulting T cell responses and changes in broader immune gene expression profiles. Renca is a BALB/c mice syngeneic tumor that has been used to model human renal cell carcinoma In this study, T cell subsets were examined in tumors and draining lymph nodes of mice treated with localized PD-1 with and without the addition of adenosine deaminase (ADA), an enzyme that catabolizes adenosine (ADO), identified as an immune checkpoint in several types of human cancers. The biologics, aPD1, or aPD1 with adenosine deaminase (aPD1/ADA), were formulated with the self-assembling peptides Z15_EAK to enhance retention near the tumor inoculation site. We found that both aPD1 and aPD1/ADA skewed the local immune milieu towards an immune stimulatory phenotype by reducing Tregs, increasing CD8 T cell infiltration, and upregulating IFNɣ. Analysis of tumor specimens using bulk RNA-Seq confirmed the impact of the localized aPD1 treatment and revealed differential gene expressions elicited by the loco-regional treatment. The effects of ADA and Z15_EAK were limited to tumor growth delay and lymph node enlargement. These results support the notion of expanding the use of locoregional PD-1 blockade in solid tumors.
Keywords: EAK16-II; RENCA; hydrogel; immune checkpoint blockade; peritumoral delivery; self-assembling peptides.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


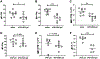
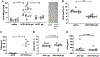

Similar articles
-
Co-delivery of dendritic cell vaccine and anti-PD-1 antibody with cryomicroneedles for combinational immunotherapy.Bioeng Transl Med. 2022 Nov 27;8(5):e10457. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10457. eCollection 2023 Sep. Bioeng Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 37693072 Free PMC article.
-
Oncolytic vaccinia virus injected intravenously sensitizes pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors and metastases to immune checkpoint blockade.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2021 Dec 21;24:299-318. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2021.12.016. eCollection 2022 Mar 17. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2021. PMID: 35118189 Free PMC article.
-
Photothermal therapy mediated by phase-transformation nanoparticles facilitates delivery of anti-PD1 antibody and synergizes with antitumor immunotherapy for melanoma.J Control Release. 2019 Jul 28;306:15-28. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.05.036. Epub 2019 May 25. J Control Release. 2019. PMID: 31132380
-
Efficacy of PD-1 blockade in cervical cancer is related to a CD8+FoxP3+CD25+ T-cell subset with operational effector functions despite high immune checkpoint levels.J Immunother Cancer. 2019 Feb 12;7(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0526-z. J Immunother Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30755279 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Tumor Growth and Sensitization to Sunitinib by RNA Interference Targeting Programmed Death-ligand 1 in Mouse Renal Cell Carcinoma RenCa Model.Anticancer Res. 2019 Sep;39(9):4737-4742. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.13656. Anticancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31519573
Cited by
-
Fibril-Guided Three-Dimensional Assembly of Human Fibroblastic Reticular Cells.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024 Jun 17;7(6):3953-3963. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.4c00331. Epub 2024 May 28. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024. PMID: 38805413 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blay J, White TD, and Hoskin DW (1997). The Extracellular Fluid of Solid Carcinomas Contains Immunosuppressive Concentrations of Adenosine. Cancer Res. 57 (13), 2602–2605. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
