Functional and Structural Characterization of OXA-935, a Novel OXA-10-Family β-Lactamase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 36129295
- PMCID: PMC9578422
- DOI: 10.1128/aac.00985-22
Functional and Structural Characterization of OXA-935, a Novel OXA-10-Family β-Lactamase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
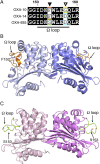
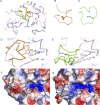
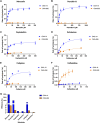
Resistance to antipseudomonal penicillins and cephalosporins is often driven by the overproduction of the intrinsic β-lactamase AmpC. However, OXA-10-family β-lactamases are a rich source of resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. OXA β-lactamases have a propensity for mutation that leads to extended spectrum cephalosporinase and carbapenemase activity. In this study, we identified isolates from a subclade of the multidrug-resistant (MDR) high risk P. aeruginosa clonal complex CC446 with a resistance to ceftazidime. A genomic analysis revealed that these isolates harbored a plasmid containing a novel allele of blaOXA-10, named blaOXA-935, which was predicted to produce an OXA-10 variant with two amino acid substitutions: an aspartic acid instead of a glycine at position 157 and a serine instead of a phenylalanine at position 153. The G157D mutation, present in OXA-14, is associated with the resistance of P. aeruginosa to ceftazidime. Compared to OXA-14, OXA-935 showed increased catalytic efficiency for ceftazidime. The deletion of blaOXA-935 restored the sensitivity to ceftazidime, and susceptibility profiling of P. aeruginosa laboratory strains expressing blaOXA-935 revealed that OXA-935 conferred ceftazidime resistance. To better understand the impacts of the variant amino acids, we determined the crystal structures of OXA-14 and OXA-935. Compared to OXA-14, the F153S mutation in OXA-935 conferred increased flexibility in the omega (Ω) loop. Amino acid changes that confer extended spectrum cephalosporinase activity to OXA-10-family β-lactamases are concerning, given the rising reliance on novel β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor combinations, such as ceftolozane-tazobactam and ceftazidime-avibactam, to treat MDR P. aeruginosa infections.
Keywords: OXA-β-lactamase; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; antimicrobial resistance; ceftazidime; crystal structure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Challenging Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Evolution of Resistance (OXA-681) during Treatment of a Long-Term Nosocomial Infection Caused by a Pseudomonas aeruginosa ST175 Clone.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019 Sep 23;63(10):e01110-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01110-19. Print 2019 Oct. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019. PMID: 31383659 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms driving the in vivo development of OXA-10-mediated resistance to ceftolozane/tazobactam and ceftazidime/avibactam during treatment of XDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021 Jan 1;76(1):91-100. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkaa396. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021. PMID: 33083833
-
Deciphering the Evolution of Cephalosporin Resistance to Ceftolozane-Tazobactam in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.mBio. 2018 Dec 11;9(6):e02085-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02085-18. mBio. 2018. PMID: 30538183 Free PMC article.
-
Cefiderocol: A Siderophore Cephalosporin with Activity Against Carbapenem-Resistant and Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacilli.Drugs. 2019 Feb;79(3):271-289. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-1055-2. Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30712199 Review.
-
The ideal patient profile for new beta-lactam/beta-lactamase inhibitors.Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2018 Dec;31(6):587-593. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0000000000000490. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 30299359 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural and Dynamic Features of Acinetobacter baumannii OXA-66 β-Lactamase Explain Its Stability and Evolution of Novel Variants.J Mol Biol. 2024 Jun 15;436(12):168603. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2024.168603. Epub 2024 May 8. J Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38729259
-
Prioritization of Critical Factors for Surveillance of the Dissemination of Antibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 15;24(20):15209. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015209. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural insights into alterations in the substrate spectrum of serine-β-lactamase OXA-10 from Pseudomonas aeruginosa by single amino acid substitutions.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2024 Dec;13(1):2412631. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2024.2412631. Epub 2024 Oct 22. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2024. PMID: 39361442 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of fortimicin antibiotic combinations against MDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa and resistome analysis of a whole genome sequenced pan-drug resistant isolate.BMC Microbiol. 2024 May 14;24(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03316-2. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38745145 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pincus NB, Bachta KER, Ozer EA, Allen JP, Pura ON, Qi C, Rhodes NJ, Marty FM, Pandit A, Mekalanos JJ, Oliver A, Hauser AR. 2020. Long-term persistence of an extensively drug-resistant subclade of globally distributed Pseudomonas aeruginosa clonal complex 446 in an academic medical center. Clin Infect Dis 71:1524–1531. 10.1093/cid/ciz973. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NCI CCSG P30 CA060553/HHS | NIH | National Cancer Institute (NCI)
- R21 AI129167/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI135964/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008061/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI053674/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RO1 AI118257/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- GM118187/HHS | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- T32 GM008152/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI118257/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI124316/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN272017000060C/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- P30 CA060553/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM121176/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM118187/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

