Ufl1 deficiency causes skin pigmentation by up-regulation of Endothelin-1
- PMID: 36120581
- PMCID: PMC9478483
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.961675
Ufl1 deficiency causes skin pigmentation by up-regulation of Endothelin-1
Abstract
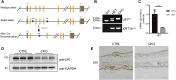
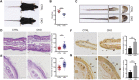
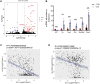
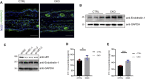
Ufmylation (UFM1 modification) is a newly identified ubiquitin-like modification system involved in numerous cellular processes. However, the regulatory mechanisms and biological functions of this modification remain mostly unknown. We have recently reported that Ufmylation family genes have frequent somatic copy number alterations in human cancer including melanoma, suggesting involvement of Ufmylation in skin function and disease. UFL1 is the only known Ufmylation E3-like ligase. In this study, we generated the skin-specific Ufl1 knockout mice and show that ablation of Ufl1 caused epidermal thickening, pigmentation and shortened life span. RNA-Seq analysis indicated that Ufl1 deletion resulted in upregulation of the genes involved in melanin biosynthesis. Mechanistically, we found that Endothelin-1 (ET-1) is a novel substrate of Ufmylation and this modification regulates ET-1 stability, and thereby deletion of Ufl1 upregulates the expression and secretion of ET-1, which in turn results in up-regulation of genes in melanin biosynthesis and skin pigmentation. Our findings establish the role of Ufl1 in skin pigmentation through Ufmylation modification of ET-1 and provide opportunities for therapeutic intervention of skin diseases.
Keywords: Ufl1; Ufl1f/f KRT14Cre/+; Ufmylation modification; endothelin-1; pigmentation.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Xu, Wang, Mao, Liu, Zhu, Cong and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
UFL1, a UFMylation E3 ligase, plays a crucial role in multiple cellular stress responses.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 10;14:1123124. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1123124. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36843575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
UFL1 ablation in T cells suppresses PD-1 UFMylation to enhance anti-tumor immunity.Mol Cell. 2024 Mar 21;84(6):1120-1138.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.01.024. Epub 2024 Feb 19. Mol Cell. 2024. PMID: 38377992
-
Ufl1/RCAD, a Ufm1 E3 ligase, has an intricate connection with ER stress.Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Aug 15;135:760-767. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.170. Epub 2019 May 23. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019. PMID: 31129212 Review.
-
A non-canonical scaffold-type E3 ligase complex mediates protein UFMylation.EMBO J. 2022 Nov 2;41(21):e111015. doi: 10.15252/embj.2022111015. Epub 2022 Sep 19. EMBO J. 2022. PMID: 36121123 Free PMC article.
-
RCAD/Ufl1, a Ufm1 E3 ligase, is essential for hematopoietic stem cell function and murine hematopoiesis.Cell Death Differ. 2015 Dec;22(12):1922-34. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.51. Epub 2015 May 8. Cell Death Differ. 2015. PMID: 25952549 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Expression of Endothelin-1, Endothelin Receptor-A, and Endothelin Receptor-B in facial melasma compared to adjacent skin.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023 Oct 12;16:2847-2853. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S402168. eCollection 2023. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37850109 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

