Reproductive history differs by molecular subtypes of breast cancer among women aged ≤ 50 years in Scotland diagnosed 2009-2016: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 36116093
- PMCID: PMC9581868
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-022-06721-1
Reproductive history differs by molecular subtypes of breast cancer among women aged ≤ 50 years in Scotland diagnosed 2009-2016: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: The aetiology of breast cancers diagnosed ≤ 50 years of age remains unclear. We aimed to compare reproductive risk factors between molecular subtypes of breast cancer, thereby suggesting possible aetiologic clues, using routinely collected cancer registry and maternity data in Scotland.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study of 4108 women aged ≤ 50 years with primary breast cancer diagnosed between 2009 and 2016 linked to maternity data. Molecular subtypes of breast cancer were defined using immunohistochemistry (IHC) tumour markers, oestrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2), and tumour grade. Age-adjusted polytomous logistic regression models were used to estimate odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) for the association of number of births, age at first birth and time since last birth with IHC-defined breast cancer subtypes. Luminal A-like was the reference compared to luminal B-like (HER2-), luminal B-like (HER2+), HER2-overexpressed and triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
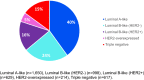
Results: Mean (SD) for number of births, age at first birth and time since last birth was 1.4 (1.2) births, 27.2 (6.1) years and 11.0 (6.8) years, respectively. Luminal A-like was the most common subtype (40%), while HER2-overexpressed and TNBC represented 5% and 15% of cases, respectively. Larger numbers of births were recorded among women with HER2-overexpressed and TNBC compared with luminal A-like tumours (> 3 vs 0 births, OR 1.87, 95%CI 1.18-2.96; OR 1.44, 95%CI 1.07-1.94, respectively). Women with their most recent birth > 10 years compared to < 2 years were less likely to have TNBC tumours compared to luminal A-like (OR 0.63, 95%CI 0.41-0.97). We found limited evidence for differences by subtype with age at first birth.
Conclusion: Number of births and time since last birth differed by molecular subtypes of breast cancer among women aged ≤ 50 years. Analyses using linked routine electronic medical records by molecularly defined tumour pathology data can be used to investigate the aetiology and prognosis of cancer.
Keywords: Age at first birth; Breast cancer; ER status; HER2; Molecular subtypes; Parity; Reproductive factors; Time since last birth.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Parity, hormones and breast cancer subtypes - results from a large nested case-control study in a national screening program.Breast Cancer Res. 2017 Jan 23;19(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13058-016-0798-x. Breast Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28114999 Free PMC article.
-
Reproductive Risk Factors Associated with Breast Cancer Molecular Subtypes among Young Women in Northern China.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Apr 6;2020:5931529. doi: 10.1155/2020/5931529. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32337260 Free PMC article.
-
Reproductive characteristics, menopausal status, race and ethnicity, and risk of breast cancer subtypes defined by ER, PR and HER2 status: the Breast Cancer Etiology in Minorities study.Breast Cancer Res. 2024 May 31;26(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s13058-024-01834-5. Breast Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38822357 Free PMC article.
-
Reproductive behaviors and risk of developing breast cancer according to tumor subtype: A systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiological studies.Cancer Treat Rev. 2016 Sep;49:65-76. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2016.07.006. Epub 2016 Jul 29. Cancer Treat Rev. 2016. PMID: 27529149 Review.
-
The influence of receptor expression and clinical subtypes on baseline [18F]FDG uptake in breast cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis.EJNMMI Res. 2023 Jan 23;13(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13550-023-00953-y. EJNMMI Res. 2023. PMID: 36689007 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A contemporary review of breast cancer risk factors and the role of artificial intelligence.Front Oncol. 2024 Apr 18;14:1356014. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1356014. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38699635 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

