A feasibility study of a randomized controlled trial protocol to assess the impact of an eHealth intervention on the provision of dietary advice in primary care
- PMID: 36104747
- PMCID: PMC9472390
- DOI: 10.1186/s40814-022-01168-z
A feasibility study of a randomized controlled trial protocol to assess the impact of an eHealth intervention on the provision of dietary advice in primary care
Abstract
Background: Canadian sodium intakes remain high despite population-wide sodium reduction initiatives, highlighting the need for personal action in reducing dietary sodium. eHealth interventions support patients in dietary change and assist clinicians in decision-making and delivering care, including provision of advice. To date, impact of diet-focused eHealth tools, like the Sodium Calculator (SC) dietary screening tool, on clinical outcomes has received minimal examination. This study assessed feasibility of a randomized controlled trial (RCT) protocol to examine the impact of the SC, a physician-focused intervention, on the quality of dietary sodium reduction advice provided by physicians to their patients with hypertension.
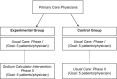
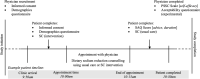
Methods: Primary care physicians from community-based primary care clinics were randomized to one of two groups: (1) 'usual care' for dietary sodium counselling or (2) dietary sodium counselling using the SC ('experimental group'). The primary endpoint was protocol feasibility defined by the following outcomes: process (e.g. recruitment, retention, protocol adherence, acceptability of intervention), resources (e.g. needs, impact on workflow), and management (e.g. staff requirements). Outcomes were assessed using direct observation, interviews, and questionnaires with patients, physicians, and clinic staff.
Results: Seven physicians (n = 4 in experimental group, n = 3 in usual care group) and 65 patients with hypertension (48.5% men, 69.8 ± 10.1 years) successfully participated. The main challenges identified is related to recruitment rate (48% for patients, 20% for physicians) and physician protocol adherence (76%). These improved with minor protocol modifications. There were several areas of protocol success such as no disruption to physician workflow, hiring clinic nurses as research staff, having a physician site lead to support physician recruitment, and a 'Protocol Prompt Form' to increase physician protocol adherence. Importantly, there was a high degree of acceptability of the SC intervention among experimental group physicians [n = 3 (75%)].
Conclusions: The modified RCT protocol was considered feasible. The identified successes can be leveraged, and the risks can be mitigated, during implementation of a full-scale RCT. Assessment of this RCT protocol is an important step in understanding the effectiveness of diet-focused eHealth tools to supporting physician self-efficacy in assessing, monitoring, and implementing dietary advice in routine clinical practice and supporting patients in effective behaviour change.
Keywords: Dietary advice; Feasibility of randomized controlled trial; Physician counselling; Sodium reduction; eHealth interventions.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative behavioural intervention to reduce drinking before elective orthopaedic surgery: the PRE-OP BIRDS feasibility RCT.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Mar;24(12):1-176. doi: 10.3310/hta24120. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32131964 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Evidence Brief: The Quality of Care Provided by Advanced Practice Nurses [Internet].Washington (DC): Department of Veterans Affairs (US); 2014 Sep. Washington (DC): Department of Veterans Affairs (US); 2014 Sep. PMID: 27606392 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Digital interventions for hypertension and asthma to support patient self-management in primary care: the DIPSS research programme including two RCTs [Internet].Southampton (UK): National Institute for Health and Care Research; 2022 Dec. Southampton (UK): National Institute for Health and Care Research; 2022 Dec. PMID: 36538606 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Sexual risk reduction interventions for patients attending sexual health clinics: a mixed-methods feasibility study.Health Technol Assess. 2019 Mar;23(12):1-122. doi: 10.3310/hta23120. Health Technol Assess. 2019. PMID: 30916641 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Development of a nurse-led decision counseling program for improving hepatocellular carcinoma screening: A typology-guided feasibility study.Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs. 2023 Mar 9;10(6):100215. doi: 10.1016/j.apjon.2023.100215. eCollection 2023 Jun. Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs. 2023. PMID: 37305610 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Guideline: sodium intake for adults and children. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2012. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK133309/. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources