Roles of Natriuretic Peptides and the Significance of Neprilysin in Cardiovascular Diseases
- PMID: 36101398
- PMCID: PMC9312343
- DOI: 10.3390/biology11071017
Roles of Natriuretic Peptides and the Significance of Neprilysin in Cardiovascular Diseases
Abstract
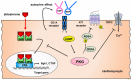
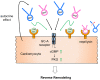
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) and brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) activate the guanylyl cyclase A receptor (GC-A), which synthesizes the second messenger cGMP in a wide variety of tissues and cells. C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP) activates the cGMP-producing guanylyl cyclase B receptor (GC-B) in chondrocytes, endothelial cells, and possibly smooth muscle cells, cardiomyocytes, and cardiac fibroblasts. The development of genetically modified mice has helped elucidate the physiological roles of natriuretic peptides via GC-A or GC-B. These include the hormonal effects of ANP/BNP in the vasculature, autocrine effects of ANP/BNP in cardiomyocytes, and paracrine effects of CNP in the vasculature and cardiomyocytes. Neprilysin (NEP) is a transmembrane neutral endopeptidase that degrades the three natriuretic peptides. Recently, mice overexpressing NEP, specifically in cardiomyocytes, revealed that local cardiac NEP plays a vital role in regulating natriuretic peptides in the heart tissue. Since NEP inhibition is a clinically accepted approach for heart failure treatment, the physiological roles of natriuretic peptides have regained attention. This article focuses on the physiological roles of natriuretic peptides elucidated in mice with GC-A or GC-B deletion, the significance of NEP in natriuretic peptide metabolism, and the long-term effects of angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI) on cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: cardiac remodeling; heart failure; natriuretic peptide; neprilysin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. Saito Y. has received research funds from Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., Novartis Pharma K.K.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neutral endopeptidase inhibition potentiates the effects of natriuretic peptides in renin transgenic rats.Hypertens Res. 1996 Dec;19(4):229-38. doi: 10.1291/hypres.19.229. Hypertens Res. 1996. PMID: 8986453
-
Neutral endopeptidase (CD10) is abundantly expressed in the epididymis and localized to a distinct population of epithelial cells--its relevance for CNP degradation.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014 Jan 25;382(1):234-243. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2013.09.027. Epub 2013 Oct 4. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24099862
-
Molecular Mechanism of Blood Pressure Regulation through the Atrial Natriuretic Peptide.Biology (Basel). 2022 Sep 14;11(9):1351. doi: 10.3390/biology11091351. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36138830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of cGMP by soluble and particulate guanylyl cyclases in cultured human airway smooth muscle.Am J Physiol. 1997 Oct;273(4):L807-13. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1997.273.4.L807. Am J Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9357856
-
Angiotensin Receptor-Neprilysin Inhibitors and the Natriuretic Peptide Axis.Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2020 Jun;17(3):67-76. doi: 10.1007/s11897-020-00458-y. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2020. PMID: 32394149 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Cardiac Natriuretic Peptides in Heart Structure and Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 20;23(22):14415. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214415. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sacubitril/valsartan attenuates atrial conduction disturbance and electrophysiological heterogeneity with ameliorating fibrosis in mice.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Jan 19;11:1341601. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1341601. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38312235 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of sacubitril/valsartan on brain natriuretic peptide level and prognosis of acute cerebral infarction.PLoS One. 2023 Sep 21;18(9):e0291754. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291754. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37733793 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Transferrin-Conjugated Melittin-Loaded L-Arginine-Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Mitigating Beta-Amyloid Pathology of the 5XFAD Mouse Brain.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 6;24(19):14954. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914954. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834402 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Significance of B-Type Natriuretic Peptide and N-Terminal Pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide in Pediatric Patients: Insights into Their Utility in the Presence or Absence of Pre-Existing Heart Conditions.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 12;25(16):8781. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168781. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201467 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kisch B. Electron microscopy of the atrium of the heart. I. Guinea Pig. Exp. Med. Surg. 1956;14:99–112. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

