Modulation of Host-Parasite Interactions with Small Molecules Targeting Schistosoma mansoni microRNAs
- PMID: 36098656
- PMCID: PMC9578036
- DOI: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.2c00360
Modulation of Host-Parasite Interactions with Small Molecules Targeting Schistosoma mansoni microRNAs
Abstract
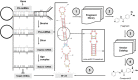
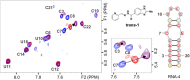
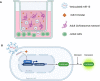
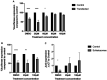
Parasites use different strategies of communication with their hosts. One communication channel that has been studied in recent years is the use of vesicle microRNAs to influence the host immune system by trematodes. sma-microRNA-10, secreted from Schistosoma mansoni, has been shown to influence the fate of host T-cells through manipulation of the NF-κB pathway. We have identified low molecular weight tool compounds that can interfere with this microRNA-mediated manipulation of the host immune system. We used a fragment-based screening approach by means of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) to identify binders to the precursor of the parasite sma-microRNA-10 present in their extracellular vesicles. The small fragments identified were used to select larger molecules. These molecules were shown to counteract the inhibition of NF-κB activity by sma-microRNA-10 in cell-based assays.
Keywords: FBS; NMR; host−parasite; microRNA; schistosome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): S.K. is an employee of EMD Serono Research and Development Institute, Inc., a business of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany. T.S. is an employee of Ares Trading S.A., an affiliate of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany. K.Z., M.J.J.B., M.G., and K.A. are employees of Saverna Therapeutics AG. S.S. and M.H. are employees of TAmiRNA GmbH.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EV-transported microRNAs of Schistosoma mansoni and Fasciola hepatica: Potential targets in definitive hosts.Infect Genet Evol. 2020 Nov;85:104528. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104528. Epub 2020 Sep 4. Infect Genet Evol. 2020. PMID: 32891875
-
Vesicle-based secretion in schistosomes: Analysis of protein and microRNA (miRNA) content of exosome-like vesicles derived from Schistosoma mansoni.Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 19;8(1):3286. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-21587-4. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29459722 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis of two populations of Schistosoma mansoni-derived extracellular vesicles: 15k pellet and 120k pellet vesicles.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2020 Mar;236:111264. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2020.111264. Epub 2020 Jan 31. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2020. PMID: 32014446
-
Polymorphic Mucin-Like Proteins in Schistosoma mansoni, a Variable Antigen and a Key Component of the Compatibility Between the Schistosome and Its Snail Host.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2015;57:91-108. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-20819-0_4. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2015. PMID: 26537378 Review.
-
Molecular crosstalk in host-parasite relationships: schistosome- and leech-host interactions.Parasitol Today. 2000 Dec;16(12):536-40. doi: 10.1016/s0169-4758(00)01787-7. Parasitol Today. 2000. PMID: 11121852 Review.
Cited by
-
Progress on the Regulation of the Host Immune Response by Parasite-Derived Exosomes.Pathogens. 2024 Jul 26;13(8):623. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13080623. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39204224 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO. WHO guideline on control and elimination of human schistosomiasis; WHO: Geneva, 2022. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

