Differential recruitment of monocyte-derived macrophages in control and stellate cell-depleted mice during recurrent carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury
- PMID: 36098042
- PMCID: PMC11296225
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.30877
Differential recruitment of monocyte-derived macrophages in control and stellate cell-depleted mice during recurrent carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury
Abstract
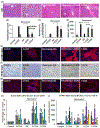
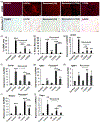
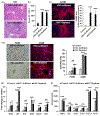
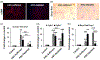
Liver depleted of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) is resistant to ischemia/reperfusion-, concanavalin A-, and acetaminophen-induced acute injury. Whether HSCs regulate carbon tetrachloride (CCl4 )-induced acute liver injury is not known. CCl4 treatment damages pericentral hepatocytes that express CCl4 -metabolizing Cyp2E1 and activates HSCs. We investigated whether HSC-depletion in mice transgenic for thymidine kinase under the glial fibrillary acidic protein promoter (GFAP-TK-Tg) confers resistance to injury and inflammation due to CCl4 rechallenge. GFAP-TK-Tg or wild type (WT) mice were administered 0.16 ml/kg CCl4 (3× at 3 days intervals), then 40 μg/g/day ganciclovir for 10 days. The treatment depletes ~70%-75% HSCs from GFAP-TK-Tg but not WT mice while the liver recovers from earlier CCl4 -induced injury. Mice were then administered CCl4 , and liver injury and inflammation were determined at 24 h. HSC-depleted and HSC-sufficient mice showed similar CCl4 -induced hepatocyte necrosis and oxidative stress. However, increase in F4/80+ macrophages, but not CD68+ cells, was greater in CCl4 rechallenged HSC-depleted compared to HSC-sufficient mice. Expression of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), CCL2, and CXCL1 increased similarly, whereas increase in interleukin-6 (IL6), IL1β, and IL10 expression was higher in CCl4 rechallenged HSC-depleted compared to HSC-sufficient mice. CCl4 rechallenge of HSC-sufficient mice rapidly activated HSCs causing significant fibrosis with increased expression of Col1a1, transforming growth factor β1 (TGFβ1), tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases 1 (TIMP1); increase in TIPM1 was much lower and metalloproteinases 13 (MMP13) greater in CCl4 rechallenged HSC-depleted mice. Interestingly, hepatic recruitment of both profibrogenic (Ly6Chi ) and antifibrogenic restorative (Ly6Clo ) macrophages, and neutrophils was significantly greater in CCl4 rechallenged HSC-depleted mice. These data suggest that CCl4 directly damages hepatocytes but HSCs regulate inflammation. Rapid fibrogenesis in CCl4 rechallenged HSC-sufficient mice recovered from earlier injury indicates that even transiently activated HSCs that had reverted to the quiescent phenotype remain primed to become reactivated.
Keywords: acute liver injury; fibrosis; inflammation; macrophages; stellate cells.
© 2022 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel mouse model of depletion of stellate cells clarifies their role in ischemia/reperfusion- and endotoxin-induced acute liver injury.J Hepatol. 2014 Feb;60(2):298-305. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.09.013. Epub 2013 Sep 20. J Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 24060854 Free PMC article.
-
A novel murine model to deplete hepatic stellate cells uncovers their role in amplifying liver damage in mice.Hepatology. 2013 Jan;57(1):339-50. doi: 10.1002/hep.26053. Hepatology. 2013. PMID: 22961591 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic stellate cells orchestrate clearance of necrotic cells in a hypoxia-inducible factor-1α-dependent manner by modulating macrophage phenotype in mice.J Immunol. 2014 Apr 15;192(8):3847-3857. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1303195. Epub 2014 Mar 17. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24639359 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-specific PPARγ deficiency establishes anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrogenic properties for this nuclear receptor in non-parenchymal liver cells.J Hepatol. 2013 Nov;59(5):1045-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.06.023. Epub 2013 Jul 2. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23831119
-
Plasticity, heterogeneity, and multifunctionality of hepatic stellate cells in liver pathophysiology.Hepatol Commun. 2024 Apr 12;8(5):e0411. doi: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000411. eCollection 2024 May 1. Hepatol Commun. 2024. PMID: 38619452 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assessing the combined impact of fatty liver-induced TGF-β1 and LPS-activated macrophages in fibrosis through a novel 3D serial section methodology.Sci Rep. 2024 May 18;14(1):11404. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-60845-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38762616 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anselmi K, Subbotin VM, Nemoto EM, & Gandhi CR (2002). Accelerated reversal of carbon tetrachloride-induced cirrhosis in rats by endothelin receptor antagonist TAK-044. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 17, 589–597. - PubMed
-
- Campana L, & Iredale JP (2015). Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors. In Gandhi CR & Pinzani M (Eds.), Stellate cells in health and disease (pp. 107–124). Elsevier/Academic Press.
-
- Dangi A, Sumpter TL, Kimura S, Stolz DB, Murase N, Raimondi G, Vodovotz Y, Huang C, Thomson AW, & Gandhi CR (2012). Selective expansion of allogeneic regulatory T cells by hepatic stellate cells: Role of endotoxin and implications for allograft tolerance. Journal of Immunology, 188, 3667–3677. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gandhi CR (2015a). Stellate cells in regulation of hepatocyte survival and function. In Gandhi CR & Pinzani M (Eds.), Stellate cells in health and disease (pp. 209–225). Elsevier/Academic Press.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

