Vandetanib Blocks the Cytokine Storm in SARS-CoV-2-Infected Mice
- PMID: 36097511
- PMCID: PMC9454268
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.2c02794
Vandetanib Blocks the Cytokine Storm in SARS-CoV-2-Infected Mice
Abstract
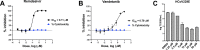
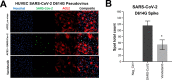
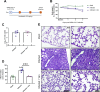
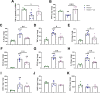
The portfolio of SARS-CoV-2 small molecule drugs is currently limited to a handful that are either approved (remdesivir), emergency approved (dexamethasone, baricitinib, paxlovid, and molnupiravir), or in advanced clinical trials. Vandetanib is a kinase inhibitor which targets the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR), the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), as well as the RET-tyrosine kinase. In the current study, it was tested in different cell lines and showed promising results on inhibition versus the toxic effect on A549-hACE2 cells (IC50 0.79 μM) while also showing a reduction of >3 log TCID50/mL for HCoV-229E. The in vivo efficacy of vandetanib was assessed in a mouse model of SARS-CoV-2 infection and statistically significantly reduced the levels of IL-6, IL-10, and TNF-α and mitigated inflammatory cell infiltrates in the lungs of infected animals but did not reduce viral load. Vandetanib also decreased CCL2, CCL3, and CCL4 compared to the infected animals. Vandetanib additionally rescued the decreased IFN-1β caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection in mice to levels similar to that in uninfected animals. Our results indicate that the FDA-approved anticancer drug vandetanib is worthy of further assessment as a potential therapeutic candidate to block the COVID-19 cytokine storm.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): S.E. and A.C.P. are employees of Collaborations Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vandetanib Reduces Inflammatory Cytokines and Ameliorates COVID-19 in Infected Mice.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 Dec 20:2021.12.16.472155. doi: 10.1101/2021.12.16.472155. bioRxiv. 2021. PMID: 34981062 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Combining the multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor vandetanib with the antiestrogen fulvestrant enhances its antitumor effect in non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2012 Mar;7(3):485-95. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31824177ea. J Thorac Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22258476 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Jinzhen granule on two coronaviruses: The novel SARS-CoV-2 and the HCoV-229E and the evidences for their mechanisms of action.Phytomedicine. 2022 Jan;95:153874. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153874. Epub 2021 Dec 11. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 34923232 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of CCR5 signaling to treat COVID-19-associated cytokine storm: Case series of four critically ill patients treated with leronlimab.J Transl Autoimmun. 2021;4:100083. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2021.100083. Epub 2021 Jan 6. J Transl Autoimmun. 2021. PMID: 33521616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vandetanib (ZD6474), a dual inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinases: current status and future directions.Oncologist. 2009 Apr;14(4):378-90. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2008-0261. Epub 2009 Apr 6. Oncologist. 2009. PMID: 19349511 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting Human Proteins for Antiviral Drug Discovery and Repurposing Efforts: A Focus on Protein Kinases.Viruses. 2023 Feb 19;15(2):568. doi: 10.3390/v15020568. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36851782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of an isoxazole-3-carboxamide analog of pleconaril in mouse models of Enterovirus-D68 and Coxsackie B5.Antiviral Res. 2023 Aug;216:105654. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2023.105654. Epub 2023 Jun 14. Antiviral Res. 2023. PMID: 37327878 Free PMC article.
-
Growth hormone-releasing hormone receptor antagonist MIA-602 attenuates cardiopulmonary injury induced by BSL-2 rVSV-SARS-CoV-2 in hACE2 mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Nov 28;120(48):e2308342120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2308342120. Epub 2023 Nov 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37983492 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of PLpro and Mpro Inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2.ACS Omega. 2023 Jun 14;8(25):22603-22612. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c01110. eCollection 2023 Jun 27. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37387790 Free PMC article.
-
C5aR1 signaling triggers lung immunopathology in COVID-19 through neutrophil extracellular traps.J Clin Invest. 2023 Jun 15;133(12):e163105. doi: 10.1172/JCI163105. J Clin Invest. 2023. PMID: 37104043 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kalil A. C.; Patterson T. F.; Mehta A. K.; Tomashek K. M.; Wolfe C. R.; Ghazaryan V.; Marconi V. C.; Ruiz-Palacios G. M.; Hsieh L.; Kline S.; Tapson V.; Iovine N. M.; Jain M. K.; Sweeney D. A.; El Sahly H. M.; Branche A. R.; Regalado Pineda J.; Lye D. C.; Sandkovsky U.; Luetkemeyer A. F.; Cohen S. H.; Finberg R. W.; Jackson P. E.H.; Taiwo B.; Paules C. I.; Arguinchona H.; Erdmann N.; Ahuja N.; Frank M.; Oh M.-d.; Kim E.-S.; Tan S. Y.; Mularski R. A.; Nielsen H.; Ponce P. O.; Taylor B. S.; Larson L.; Rouphael N. G.; Saklawi Y.; Cantos V. D.; Ko E. R.; Engemann J. J.; Amin A. N.; Watanabe M.; Billings J.; Elie M.-C.; Davey R. T.; Burgess T. H.; Ferreira J.; Green M.; Makowski M.; Cardoso A.; de Bono S.; Bonnett T.; Proschan M.; Deye G. A.; Dempsey W.; Nayak S. U.; Dodd L. E.; Beigel J. H. Baricitinib plus Remdesivir for Hospitalized Adults with Covid-19. N Engl J. Med. 2021, 384 (9), 795–807. 10.1056/NEJMoa2031994. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

