Hamster organotypic kidney culture model of early-stage SARS-CoV-2 infection highlights a two-step renal susceptibility
- PMID: 36093433
- PMCID: PMC9452794
- DOI: 10.1177/20417314221122130
Hamster organotypic kidney culture model of early-stage SARS-CoV-2 infection highlights a two-step renal susceptibility
Abstract
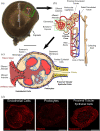
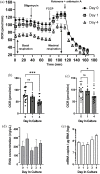
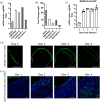
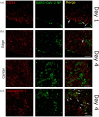
Kidney pathology is frequently reported in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, the pandemic disease caused by the Severe acute respiratory coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). However, due to a lack of suitable study models, the events occurring in the kidney during the earliest stages of infection remain unknown. We have developed hamster organotypic kidney cultures (OKCs) to study the early stages of direct renal infection. OKCs maintained key renal structures in their native three-dimensional arrangement. SARS-CoV-2 productively replicated in hamster OKCs, initially targeting endothelial cells and later disseminating into proximal tubules. We observed a delayed interferon response, markers of necroptosis and pyroptosis, and an early repression of pro-inflammatory cytokines transcription followed by a strong later upregulation. While it remains an open question whether an active replication of SARS-CoV-2 takes place in the kidneys of COVID-19 patients with AKI, our model provides new insights into the kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 kidney infection and can serve as a powerful tool for studying kidney infection by other pathogens and testing the renal toxicity of drugs.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; kidney; organotypic cultures.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Type I and Type III Interferons Restrict SARS-CoV-2 Infection of Human Airway Epithelial Cultures.J Virol. 2020 Sep 15;94(19):e00985-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00985-20. Print 2020 Sep 15. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32699094 Free PMC article.
-
Coronavirus Disease 19 Infection Does Not Result in Acute Kidney Injury: An Analysis of 116 Hospitalized Patients from Wuhan, China.Am J Nephrol. 2020;51(5):343-348. doi: 10.1159/000507471. Epub 2020 Mar 31. Am J Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32229732 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Causes Acute Kidney Injury by Directly Infecting Renal Tubules.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 May 31;9:664868. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.664868. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34136484 Free PMC article.
-
Kidney injury in COVID-19 patients, drug development and their renal complications: Review study.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Oct;142:111966. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111966. Epub 2021 Jul 27. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 34333286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV replication and pathogenesis in an in vitro model of the human conducting airway epithelium.Virus Res. 2008 Apr;133(1):33-44. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2007.03.013. Epub 2007 Apr 23. Virus Res. 2008. PMID: 17451829 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In Silico Prediction of Hub Genes Involved in Diabetic Kidney and COVID-19 Related Disease by Differential Gene Expression and Interactome Analysis.Genes (Basel). 2022 Dec 19;13(12):2412. doi: 10.3390/genes13122412. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36553678 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Worldometer. Coronavirus cases, https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/ (2022, accessed 11 March 2022).
-
- George JA, Khoza S. SARS-CoV-2 infection and the kidneys: an evolving picture. Adv Exp Med Biol 2021; 1327: 107–118. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

