Close association between lifestyle and circulating FGF21 levels: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36093108
- PMCID: PMC9453313
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.984828
Close association between lifestyle and circulating FGF21 levels: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The impact of lifestyle factors on circulating fibroblast growth factor 21 (cFGF21) remains unclear. We conducted this systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the association between lifestyle factors and cFGF21 levels.
Methods: We included studies that evaluated the effects of different lifestyles on cFGF21 concentration in adults, which included smoking, exercise, diets, alcohol consumption and weight loss. Random effects models or fixed effects models were used for meta-analysis to calculate the standardized mean difference (SMD) and 95% confidence interval according to the heterogeneity among studies. Study quality was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale for cohort studies, the Joanna Briggs Institution Checklist for cross-sectional studies, and the PEDro scale for experimental studies.
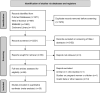
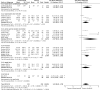
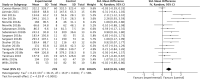
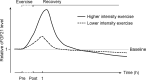
Results: A total of 50 studies with 1438 individuals were included. Overall, smoking, a hypercaloric carbohydrate-rich diet, a hypercaloric fat-rich diet, amino acid or protein restriction, excessive fructose intake and alcohol consumption significantly upregulated cFGF21 levels (p<0.05), whereas fish oil intake and calorie restriction with sufficient protein intake significantly decreased cFGF21 (p<0.05). Compared to the preexercise cFGF21 level, the cFGF21 level significantly increased within 3 hours postexercise (p<0.0001), while it significantly decreased in the blood sampled >6 h postexercise (p=0.01). Moreover, higher exercise intensity resulted in higher upregulation of cFGF21 at 1-hour post exercise (p=0.0006).
Conclusion: FGF21 could serve as a potential biomarker for the assessment of different lifestyle interventions. When it is used for this purpose, a standard study protocol needs to be established, especially taking into consideration the intervention types and the sampling time post-intervention.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42021254758, identifier CRD42021254758.
Keywords: biomarker; circulating FGF21; diet; exercise; lifestyle.
Copyright © 2022 Qian, Zhang, Yang, Nie, Yang, Luo, Wei, Guan, Huang, Yan, Ruan, Zhang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
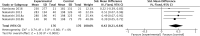


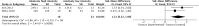

Similar articles
-
High-Level Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Concentration Is Closely Associated With an Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Aug 26;8:705273. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.705273. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34513950 Free PMC article.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of weight management interventions that include a diet component on weight-related outcomes in pregnant and postpartum women: a systematic review protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Jan;13(1):88-98. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-1812. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26447010
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of primary health education or intervention programs in improving rural women's knowledge of heart disease risk factors and changing lifestyle behaviours.Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2011 Sep;9(3):236-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-1609.2011.00226.x. Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2011. PMID: 21884451 Review.
-
The Association Between Smartphone App-Based Self-monitoring of Hypertension-Related Behaviors and Reductions in High Blood Pressure: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2022 Jul 12;10(7):e34767. doi: 10.2196/34767. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2022. PMID: 35819830 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association of NAFLD with FGF21 Polygenic Hazard Score, and Its Interaction with Protein Intake Level in Korean Adults.Nutrients. 2023 May 19;15(10):2385. doi: 10.3390/nu15102385. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37242268 Free PMC article.
-
Total serum FGF-21 levels positively relate to visceral adiposity differently from its functional intact form.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jun 20;14:1159127. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1159127. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37409233 Free PMC article.

