Recent findings in the regulation of G6PD and its role in diseases
- PMID: 36091812
- PMCID: PMC9448902
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.932154
Recent findings in the regulation of G6PD and its role in diseases
Abstract
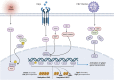
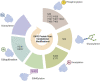
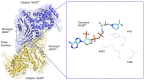
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) is the only rate-limiting enzyme in the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP). Rapidly proliferating cells require metabolites from PPP to synthesize ribonucleotides and maintain intracellular redox homeostasis. G6PD expression can be abnormally elevated in a variety of cancers. In addition, G6PD may act as a regulator of viral replication and vascular smooth muscle function. Therefore, G6PD-mediated activation of PPP may promote tumor and non-neoplastic disease progression. Recently, studies have identified post-translational modifications (PTMs) as an important mechanism for regulating G6PD function. Here, we provide a comprehensive review of various PTMs (e.g., phosphorylation, acetylation, glycosylation, ubiquitination, and glutarylation), which are identified in the regulation of G6PD structure, expression and enzymatic activity. In addition, we review signaling pathways that regulate G6PD and evaluate the role of oncogenic signals that lead to the reprogramming of PPP in tumor and non-neoplastic diseases as well as summarize the inhibitors that target G6PD.
Keywords: glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; metabolic reprogramming; pentose phosphate pathway; post-translational modifications; tumorigenesis.
Copyright © 2022 Meng, Zhang, Hao, Sun, Liu, Zhou, Wang and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Emerging Roles of the Metabolic Regulator G6PD in Human Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 7;24(24):17238. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417238. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PBX3 promotes pentose phosphate pathway and colorectal cancer progression by enhancing G6PD expression.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Aug 28;19(14):4525-4538. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.86279. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37781025 Free PMC article.
-
TRAF6-Mediated SM22α K21 Ubiquitination Promotes G6PD Activation and NADPH Production, Contributing to GSH Homeostasis and VSMC Survival In Vitro and In Vivo.Circ Res. 2015 Sep 25;117(8):684-94. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306233. Epub 2015 Aug 19. Circ Res. 2015. PMID: 26291555
-
KLF8 Promotes the Survival of Lung Adenocarcinoma During Nutrient Deprivation by Regulating the Pentose Phosphate Pathway through SIRT2.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024 Jan 18;29(1):27. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2901027. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024. PMID: 38287804
-
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase: a therapeutic target for ovarian cancer.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2023 Jul-Dec;27(8):733-743. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2023.2247558. Epub 2023 Aug 18. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2023. PMID: 37571851 Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction and disulfidptosis co-regulate neuronal cell in neuropathic pain based on bioinformatics analysis.Mol Pain. 2024 Jan-Dec;20:17448069241290114. doi: 10.1177/17448069241290114. Mol Pain. 2024. PMID: 39323309 Free PMC article.
-
KHDRBS1 regulates the pentose phosphate pathway and malignancy of GBM through SNORD51-mediated polyadenylation of ZBED6 pre-mRNA.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Nov 8;15(11):802. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07163-x. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39516455 Free PMC article.
-
Renal Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Metabolic Abnormalities During the Initial Stages of Hypertension in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats.Cells. 2024 Oct 25;13(21):1771. doi: 10.3390/cells13211771. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39513878 Free PMC article.
-
Development of the RF-GSEA Method for Identifying Disulfidptosis-Related Genes and Application in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Nov 24;45(12):9450-9470. doi: 10.3390/cimb45120593. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 38132439 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Neuronal CoQ10 Deficiency and Mitochondrial Dysfunction on a Rotenone-Induced Neuronal Cell Model of Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 16;25(12):6622. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126622. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928331 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Au S. W., Naylor C. E., Gover S., Vandeputte-Rutten L., Scopes D. A., Mason P. J., et al. (1999). Solution of the structure of tetrameric human glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase by molecular replacement. Acta Crystallogr. D. Biol. Crystallogr. 55 (4), 826–834. 10.1107/s0907444999000827 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aurora A. B., Khivansara V., Leach A., Gill J. G., Martin-Sandoval M., Yang C., et al. (2022). Loss of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase function increases oxidative stress and glutaminolysis in metastasizing melanoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 119 (6), e2120617119. 10.1073/pnas.2120617119 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

