Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): screening, treatment and survival analysis in a Brazilian series
- PMID: 36088887
- PMCID: PMC9468355
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2022.100097
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): screening, treatment and survival analysis in a Brazilian series
Abstract
Objective: The aim of the present study was to evaluate the clinical features, Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) screening, treatment modalities, and Overall Survival (OS) in a series of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma (NAFLD-HCC) Brazilian patients.
Methods: This was a cross-sectional study at the Instituto do Cancer do Estado de São Paulo, at the Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo with the approval of the local research ethics committee. NAFLD patients with HCC diagnosed, from May 2010 to May 2019, were included.
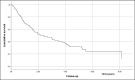
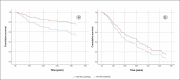
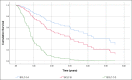
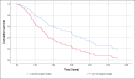
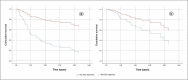
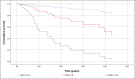
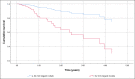
Results: A total of 131 patients were included. Risk factors for NAFLD were present in 94.7% of the patients. Only 29% of patients were in the HCC screening program before diagnosis. HCC treatment was performed in 84.7% of patients. Cumulative survival at the end of the first year was 72%, second-year 52%, and fifth-year 32%. HCC screening before diagnosis was not significantly associated with higher cumulative survival. The independent factors associated with shorter general survival were BCLC C-D, p < 0.001, and the size of the largest nodule > 42 mm, p = 0.039.
Conclusions: Although the efficacy of screening in our population regarding overall survival was hampered due to the sample size (29% had screening), BCLC stages C‒D and the size of the largest nodule larger than 42 mm were identified as independent factors of worse prognosis.
Keywords: HCC screening program; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; Overall survival; Treatment.
Copyright © 2022 HCFMUSP. Published by Elsevier España, S.L.U. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Survival after treatment with curative intent for hepatocellular carcinoma among patients with vs without non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017 Dec;46(11-12):1061-1069. doi: 10.1111/apt.14342. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28960360
-
Characterization of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) patients without cirrhosis.Hepatol Int. 2016 Jul;10(4):632-9. doi: 10.1007/s12072-015-9679-0. Epub 2015 Nov 11. Hepatol Int. 2016. PMID: 26558795
-
Alcoholic Liver Disease-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Characteristics and Comparison to General Slovak Hepatocellular Cancer Population.Curr Oncol. 2023 Mar 22;30(3):3557-3570. doi: 10.3390/curroncol30030271. Curr Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36975484 Free PMC article.
-
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease associated with hepatocellular carcinoma: An increasing concern.Indian J Med Res. 2019 Jan;149(1):9-17. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_1456_17. Indian J Med Res. 2019. PMID: 31115369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[The Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease].Korean J Gastroenterol. 2017 Jun 25;69(6):348-352. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2017.69.6.348. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28637103 Review. Korean.
References
-
- Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2018;391(10127):1301–1314. - PubMed
-
- Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, Charlton M, Cusi K, Rinella M, et al. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018;67(1):328–357. - PubMed
-
- Younossi ZM, Stepanova M, Rafiq N, Makhlouf H, Younoszai Z, Agrawal R, et al. Pathologic criteria for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: interprotocol agreement and ability to predict liver-related mortality. Hepatology. 2011;53(6):1874–1882. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

