Manufacture and Quality Control of Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Sheets for Clinical Use
- PMID: 36078137
- PMCID: PMC9454431
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11172732
Manufacture and Quality Control of Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Sheets for Clinical Use
Abstract
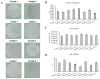
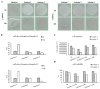
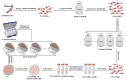
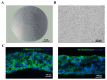
Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell (UC-MSC) sheets have attracted much attention in cell therapy. However, the culture media and coating matrix used for the preparation of UC-MSC sheets have not been safe enough to comply with current clinical drug standards. Moreover, the UC-MSC sheet preservation systems developed before did not comply with Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) regulations. In this study, the culture medium and coating matrix were developed for UC-MSC sheet production to comply with clinical drug standards. Additionally, the GMP-compliant preservation solution and method for the UC-MSC sheet were developed. Then, quality standards of the UC-MSC sheet were formulated according to national and international regulations for drugs. Finally, the production process of UC-MSC sheets on a large scale was standardized, and three batches of trial production were conducted and tested to meet the established quality standards. This research provides the possibility for clinical trials of UC-MSC sheet products in the development stage of new drugs and lays the foundation for industrial large-scale production after the new drug is launched.
Keywords: large-scale production; preservation; umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell sheet.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Study on the Umbilical Cord-Mesenchymal Stem Cell Manufacturing Using Clinical-Grade Culture Medium.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2022 Jan;28(1):23-33. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEC.2021.0207. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2022. PMID: 35018815
-
Development of a human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cell-based advanced therapy medicinal product to treat immune and/or inflammatory diseases.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Nov 13;12(1):571. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02637-7. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34774107 Free PMC article.
-
Human umbilical cord-derived stem cell sheets improve left ventricular function in rat models of ischemic heart failure.Eur J Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 15;925:174994. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.174994. Epub 2022 May 2. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35513020
-
Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells: a promising candidate for the development of advanced therapy medicinal products.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Feb 26;12(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02222-y. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 33637125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Translating mesenchymal stem cell and their exosome research into GMP compliant advanced therapy products: Promises, problems and prospects.Med Res Rev. 2024 May;44(3):919-938. doi: 10.1002/med.22002. Epub 2023 Dec 14. Med Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 38095832 Review.
Cited by
-
MSCohi-O lenses for long-term retention of mesenchymal stem cells on ocular surface as a therapeutic approach for chronic ocular graft-versus-host disease.Stem Cell Reports. 2023 Dec 12;18(12):2356-2369. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2023.10.010. Epub 2023 Nov 9. Stem Cell Reports. 2023. PMID: 37949071 Free PMC article.
-
Potency assays and biomarkers for cell-based advanced therapy medicinal products.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 9;14:1186224. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1186224. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37359560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of scaffold-free tissue-engineered constructs derived from mesenchymal stem cells with serum-free media for cartilage repair and long-term preservation.Cytotechnology. 2024 Oct;76(5):595-612. doi: 10.1007/s10616-024-00637-y. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Cytotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39188648
-
Engineering cell-derived extracellular matrix for peripheral nerve regeneration.Mater Today Bio. 2024 Jun 13;27:101125. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101125. eCollection 2024 Aug. Mater Today Bio. 2024. PMID: 38979129 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human dental pulp stem cells have comparable abilities to umbilical cord mesenchymal stem/stromal cells in regulating inflammation and ameliorating hepatic fibrosis.Hum Cell. 2024 Jan;37(1):204-213. doi: 10.1007/s13577-023-01004-3. Epub 2023 Nov 15. Hum Cell. 2024. PMID: 37964155
References
-
- Hsieh J.Y., Fu Y.S., Chang S.J., Tsuang Y.H., Wang H.W. Functional module analysis reveals differential osteogenic and stemness potentials in human mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow and Wharton’s jelly of umbilical cord. Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19:1895–1910. doi: 10.1089/scd.2009.0485. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abu Kasim N.H., Govindasamy V., Gnanasegaran N., Musa S., Pradeep P.J., Srijaya T.C., Aziz Z.A. Unique molecular signatures influencing the biological function and fate of post-natal stem cells isolated from different sources. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2015;9:E252–E266. doi: 10.1002/term.1663. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Christodoulou I., Kolisis F.N., Papaevangeliou D., Zoumpourlis V. Comparative Evaluation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells of Fetal (Wharton’s Jelly) and Adult (Adipose Tissue) Origin during Prolonged In Vitro Expansion: Considerations for Cytotherapy. Stem Cells Int. 2013;2013:246134. doi: 10.1155/2013/246134. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

