Expression of the C-Terminal Domain of Phospholipase Cβ3 Inhibits Signaling via Gαq-Coupled Receptors and Transient Receptor Potential Channels
- PMID: 36076982
- PMCID: PMC9455670
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23179590
Expression of the C-Terminal Domain of Phospholipase Cβ3 Inhibits Signaling via Gαq-Coupled Receptors and Transient Receptor Potential Channels
Abstract
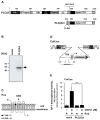
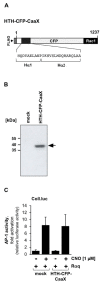
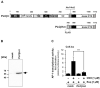
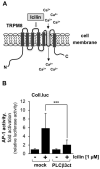
Transient receptor potential (TRP) channels are cation channels that play a regulatory role in pain and thermosensation, insulin secretion, and neurotransmission. It has been proposed that activation of TRP channels requires phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, the major substrate for phospholipase C (PLC). We investigated whether inhibition of PLCβ has an impact on TRP channel signaling. A genetic approach was used to avoid off-target effects observed when using a pharmacological PLCβ inhibitor. In this study, we show that expression of PLCβ1ct and PLCβ3ct, truncated forms of PLCβ1 or PLCβ3 that contain the C-terminal membrane binding domains, almost completely blocked the signal transduction of a Gαq-coupled designer receptor, including the phosphorylation of ERK1/2. In contrast, expression of the helix-turn-helix motif (Hα1-Hα2) of the proximal C-terminal domain of PLCβ3 did not affect Gαq-coupled receptor signaling. PLCβ3ct expression impaired signaling of the TRP channels TRPM3 and TRPM8, stimulated with either prognenolone sulfate or icilin. Thus, the C-terminal domain of PLCβ3 interacts with plasma membrane targets, most likely phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, and in this way blocks the biological activation of TRPM3 and TRPM8, which require interaction with this phospholipid. PLCβ thus regulates TRPM3 and TRPM8 channels by masking phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate with its C-terminal domain.
Keywords: ERK1/2; Gαq-coupled designer receptor; TRPM3; TRPM8; m-3M3FBS; phospholipase Cβ.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The mechanism of Gαq regulation of PLCβ3-catalyzed PIP2 hydrolysis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Nov 28;120(48):e2315011120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2315011120. Epub 2023 Nov 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37991948 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of serine 1105 by protein kinase A inhibits phospholipase Cbeta3 stimulation by Galphaq.J Biol Chem. 1998 Jul 17;273(29):18023-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.29.18023. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9660757
-
KN-93 inhibition of G protein signaling is independent of the ability of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II to phosphorylate phospholipase Cbeta3 on 537-Ser.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2001 Apr 25;175(1-2):149-56. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(01)00383-5. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2001. PMID: 11325525
-
Decoding Gαq signaling.Life Sci. 2016 May 1;152:99-106. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.03.037. Epub 2016 Mar 22. Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27012764 Review.
-
Regulation of TRP ion channels by phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2007;(179):509-25. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-34891-7_30. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17217076 Review.
Cited by
-
Signal Transduction of Transient Receptor Potential TRPM8 Channels: Role of PIP5K, Gq-Proteins, and c-Jun.Molecules. 2024 Jun 1;29(11):2602. doi: 10.3390/molecules29112602. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38893478 Free PMC article.
-
Calmodulin Regulates Transient Receptor Potential TRPM3 and TRPM8-Induced Gene Transcription.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 26;24(9):7902. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097902. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175607 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

