Flavonol glycoside complanatoside A requires FOXO/DAF-16, NRF2/SKN-1, and HSF-1 to improve stress resistances and extend the life span of Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 36071837
- PMCID: PMC9441740
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.931886
Flavonol glycoside complanatoside A requires FOXO/DAF-16, NRF2/SKN-1, and HSF-1 to improve stress resistances and extend the life span of Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
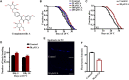
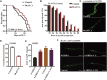
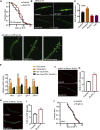
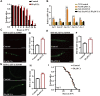
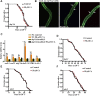
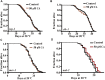
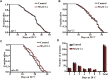
Aging is associated with the increased risk of most age-related diseases in humans. Complanatoside A (CA) is a flavonoid compound isolated from the herbal medicine Semen Astragali Complanati. CA was reported to have potential anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative activities. In this study, we investigated whether CA could increase the stress resistance capability and life span of Caenorhabditis elegans. Our results showed that CA could extend the longevity of C. elegans in a dosage-dependent manner, while 50 μM of CA has the best effect and increased the life span of C. elegans by about 16.87%. CA also improved the physiological functions in aging worms, such as enhanced locomotor capacity, and reduced the accumulation of the aging pigment. CA could also reduce the accumulation of toxic proteins (α-synuclein and β-amyloid) and delay the onset of neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease, in models of C. elegans. Further investigation has revealed that CA requires DAF-16/FOXO, SKN-1, and HSF-1 to extend the life span of C. elegans. CA could increase the antioxidation and detoxification activities regulated by transcription factor SKN-1 and the heat resistance by activating HSF-1 that mediated the expression of the chaperone heat shock proteins. Our results suggest that CA is a potential antiaging agent worth further research for its pharmacological mechanism and development for pharmaceutical applications.
Keywords: Caenorhabditis elegans; DAF-16/FOXO; aging; complanatoside A; neurodegenerative diseases; oxidative stress; proteostasis.
Copyright © 2022 Tan, Zheng, Huang, Jin, Li, Wu and Luo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
D-chiro-inositol increases antioxidant capacity and longevity of Caenorhabditis elegans via activating Nrf-2/SKN-1 and FOXO/DAF-16.Exp Gerontol. 2023 May;175:112145. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2023.112145. Epub 2023 Mar 20. Exp Gerontol. 2023. PMID: 36921677
-
Orientin Prolongs the Longevity of Caenorhabditis elegans and Postpones the Development of Neurodegenerative Diseases via Nutrition Sensing and Cellular Protective Pathways.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Feb 21;2022:8878923. doi: 10.1155/2022/8878923. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35237385 Free PMC article.
-
Tectochrysin increases stress resistance and extends the lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans via FOXO/DAF-16.Biogerontology. 2020 Oct;21(5):669-682. doi: 10.1007/s10522-020-09884-w. Epub 2020 Jun 6. Biogerontology. 2020. PMID: 32506187
-
Uric acid induces stress resistance and extends the life span through activating the stress response factor DAF-16/FOXO and SKN-1/NRF2.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Feb 12;12(3):2840-2856. doi: 10.18632/aging.102781. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 32074508 Free PMC article.
-
HSF-1: Guardian of the Proteome Through Integration of Longevity Signals to the Proteostatic Network.Front Aging. 2022 Jul 8;3:861686. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2022.861686. eCollection 2022. Front Aging. 2022. PMID: 35874276 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
APPA Increases Lifespan and Stress Resistance via Lipid Metabolism and Insulin/IGF-1 Signal Pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 5;24(18):13682. doi: 10.3390/ijms241813682. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37761985 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant and Stress Resistance Properties of Flavonoids from Chinese Sea Buckthorn Leaves from the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jun 25;13(7):763. doi: 10.3390/antiox13070763. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061832 Free PMC article.
-
Natural antioxidants that act against Alzheimer's disease through modulation of the NRF2 pathway: a focus on their molecular mechanisms of action.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jul 3;14:1217730. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1217730. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37465125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
4,4'-methylenediphenol reduces Aβ-induced toxicity in a Caenorhabditis elegans model of Alzheimer's disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2024 May 30;16:1393721. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1393721. eCollection 2024. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38872629 Free PMC article.
-
P-hydroxybenzaldehyde protects Caenorhabditis elegans from oxidative stress and β-amyloid toxicity.Front Aging Neurosci. 2024 May 22;16:1414956. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1414956. eCollection 2024. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38841104 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acharya S. N., Kastelic J. P., Beauchemin K. A., Messenger D. F. (2006). A review of research progress on cicer milkvetch (Astragalus cicer L.) Can. J. Plant Sci. 86 (1), 49–62. 10.4141/p04-174 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

