Methionine metabolism controls the B cell EBV epigenome and viral latency
- PMID: 36070681
- PMCID: PMC9482757
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2022.08.008
Methionine metabolism controls the B cell EBV epigenome and viral latency
Abstract
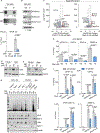
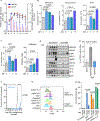
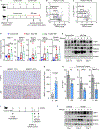
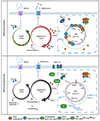
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) subverts host epigenetic pathways to switch between viral latency programs, colonize the B cell compartment, and reactivate. Within memory B cells, the reservoir for lifelong infection, EBV genomic DNA and histone methylation marks restrict gene expression. But this epigenetic strategy also enables EBV-infected tumors, including Burkitt lymphomas, to evade immune detection. Little is known about host cell metabolic pathways that support EBV epigenome landscapes. We therefore used amino acid restriction, metabolomic, and CRISPR approaches to identify that an abundant methionine supply and interconnecting methionine and folate cycles maintain Burkitt EBV gene silencing. Methionine restriction, or methionine cycle perturbation, hypomethylated EBV genomes and de-repressed latent membrane protein and lytic gene expression. Methionine metabolism also shaped EBV latency gene regulation required for B cell immortalization. Dietary methionine restriction altered murine Burkitt xenograft metabolomes and de-repressed EBV immunogens in vivo. These results highlight epigenetic/immunometabolism crosstalk supporting the EBV B cell life cycle and suggest therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: dietary amino acid restriction; folate metabolism; gamma-herpesvirus; immunometabolism; lytic reactivation; methionine cycle; methionine metabolism; one-carbon metabolism; tumor virus; viral latency.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



Comment in
-
Methionine restriction forces Epstein-Barr virus out of latency.Cell Metab. 2022 Sep 6;34(9):1229-1231. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2022.08.009. Cell Metab. 2022. PMID: 36070678
Similar articles
-
Histone Loaders CAF1 and HIRA Restrict Epstein-Barr Virus B-Cell Lytic Reactivation.mBio. 2020 Oct 27;11(5):e01063-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01063-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 33109754 Free PMC article.
-
BZLF1 governs CpG-methylated chromatin of Epstein-Barr Virus reversing epigenetic repression.PLoS Pathog. 2012 Sep;8(9):e1002902. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002902. Epub 2012 Sep 6. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22969425 Free PMC article.
-
The BHLF1 Locus of Epstein-Barr Virus Contributes to Viral Latency and B-Cell Immortalization.J Virol. 2020 Aug 17;94(17):e01215-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01215-20. Print 2020 Aug 17. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32581094 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic control of the Epstein-Barr lifecycle.Curr Opin Virol. 2022 Feb;52:78-88. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2021.11.013. Epub 2021 Dec 8. Curr Opin Virol. 2022. PMID: 34891084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic crossroads of the Epstein-Barr virus B-cell relationship.Curr Opin Virol. 2018 Oct;32:15-23. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2018.08.012. Epub 2018 Sep 15. Curr Opin Virol. 2018. PMID: 30227386 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Germinal center cytokine driven epigenetic control of Epstein-Barr virus latency gene expression.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Apr 29;20(4):e1011939. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011939. eCollection 2024 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38683861 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the crosstalk of epigenetic modifications and immune evasion in nasopharyngeal cancer.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023 Dec;39(6):2501-2526. doi: 10.1007/s10565-023-09830-9. Epub 2023 Sep 27. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37755585 Review.
-
Rewiring of the Host Cell Metabolome and Lipidome during Lytic Gammaherpesvirus Infection Is Essential for Infectious-Virus Production.J Virol. 2023 Jun 29;97(6):e0050623. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00506-23. Epub 2023 May 16. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 37191529 Free PMC article.
-
The significant role of amino acid metabolic reprogramming in cancer.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jul 29;22(1):380. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01760-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39069612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endemic Burkitt lymphoma avatar mouse models for exploring inter-patient tumor variation and testing targeted therapies.Life Sci Alliance. 2023 Mar 6;6(5):e202101355. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202101355. Print 2023 May. Life Sci Alliance. 2023. PMID: 36878637 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alfieri C, Birkenbach M, and Kieff E (1991). Early events in Epstein-Barr virus infection of human B lymphocytes. Virology 181, 595–608. - PubMed
-
- Ambinder RF, Robertson KD, and Tao Q (1999). DNA methylation and the Epstein-Barr virus. Semin Cancer Biol 9, 369–375. - PubMed
-
- Bjornevik K, Cortese M, Healy BC, Kuhle J, Mina MJ, Leng Y, Elledge SJ, Niebuhr DW, Scher AI, Munger KL, et al. (2022). Longitudinal analysis reveals high prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus associated with multiple sclerosis. Science 375, 296–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

