Imp interacts with Lin28 to regulate adult stem cell proliferation in the Drosophila intestine
- PMID: 36070313
- PMCID: PMC9484684
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010385
Imp interacts with Lin28 to regulate adult stem cell proliferation in the Drosophila intestine
Abstract
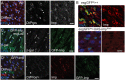
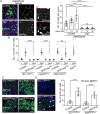
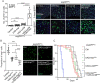
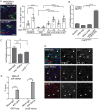
Stem cells are essential for the development and long-term maintenance of tissues and organisms. Preserving tissue homeostasis requires exquisite control of all aspects of stem cell function: cell potency, proliferation, fate decision and differentiation. RNA binding proteins (RBPs) are essential components of the regulatory network that control gene expression in stem cells to maintain self-renewal and long-term homeostasis in adult tissues. While the function of many RBPs may have been characterized in various stem cell populations, how these interact and are organized in genetic networks remains largely elusive. In this report, we show that the conserved RNA binding protein IGF2 mRNA binding protein (Imp) is expressed in intestinal stem cells (ISCs) and progenitors in the adult Drosophila midgut. We demonstrate that Imp is required cell autonomously to maintain stem cell proliferative activity under normal epithelial turnover and in response to tissue damage. Mechanistically, we show that Imp cooperates and directly interacts with Lin28, another highly conserved RBP, to regulate ISC proliferation. We found that both proteins bind to and control the InR mRNA, a critical regulator of ISC self-renewal. Altogether, our data suggests that Imp and Lin28 are part of a larger gene regulatory network controlling gene expression in ISCs and required to maintain epithelial homeostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tis11 mediated mRNA decay promotes the reacquisition of Drosophila intestinal stem cell quiescence.Dev Biol. 2017 Jun 1;426(1):8-16. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.04.013. Epub 2017 Apr 23. Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28445691 Free PMC article.
-
Paracrine Wingless signalling controls self-renewal of Drosophila intestinal stem cells.Nature. 2008 Oct 23;455(7216):1119-23. doi: 10.1038/nature07329. Epub 2008 Sep 21. Nature. 2008. PMID: 18806781
-
InR and Pi3K maintain intestinal homeostasis through STAT/EGFR and Notch signaling in enteroblasts.J Cell Biochem. 2024 Jun;125(6):e30545. doi: 10.1002/jcb.30545. Epub 2024 Mar 4. J Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38436545
-
Intestinal stem cell response to injury: lessons from Drosophila.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Sep;73(17):3337-49. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2235-9. Epub 2016 May 2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27137186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA Binding Proteins in Intestinal Epithelial Biology and Colorectal Cancer.Trends Mol Med. 2018 May;24(5):490-506. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2018.03.008. Epub 2018 Apr 5. Trends Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29627433 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lin28 is Required for Single Niche Development in the Drosophila Male Gonad.Dev Reprod. 2023 Dec;27(4):221-226. doi: 10.12717/DR.2023.27.4.221. Epub 2023 Dec 31. Dev Reprod. 2023. PMID: 38292237 Free PMC article.
-
Imp is expressed in INPs and newborn neurons where it regulates neuropil targeting in the central complex.Neural Dev. 2023 Nov 29;18(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s13064-023-00177-9. Neural Dev. 2023. PMID: 38031099 Free PMC article.
-
Nazo, the Drosophila homolog of the NBIA-mutated protein-c19orf12, is required for triglyceride homeostasis.PLoS Genet. 2024 Feb 9;20(2):e1011137. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011137. eCollection 2024 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2024. PMID: 38335241 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

