Electrochemical and biological performance of hierarchical platinum-iridium electrodes structured by a femtosecond laser
- PMID: 36065436
- PMCID: PMC9440118
- DOI: 10.1038/s41378-022-00433-8
Electrochemical and biological performance of hierarchical platinum-iridium electrodes structured by a femtosecond laser
Abstract
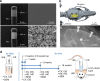
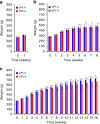
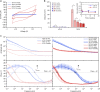
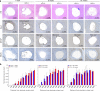
Neural electrode interfaces are essential to the stimulation safety and recording quality of various bioelectronic therapies. The recently proposed hierarchical platinum-iridium (Pt-Ir) electrodes produced by femtosecond lasers have exhibited superior electrochemical performance in vitro, but their in vivo performance is still unclear. In this study, we explored the electrochemical performance, biological response, and tissue adhesion of hierarchical Pt-Ir electrodes by implantation in adult rat brains for 1, 8, and 16 weeks. Regular smooth Pt-Ir electrodes were used as a control. The results showed that the electrochemical performance of both electrodes decreased and leveled off during implantation. However, after 16 weeks, the charge storage capacity of hierarchical electrodes stabilized at ~16.8 mC/cm2, which was 15 times that of the smooth control electrodes (1.1 mC/cm2). Moreover, the highly structured electrodes had lower impedance amplitude and cutoff frequency values. The similar histological response to smooth electrodes indicated good biocompatibility of the hierarchically structured Pt-Ir electrodes. Given their superior in vivo performance, the femtosecond laser-treated Pt-Ir electrode showed great potential for neuromodulation applications.
Keywords: Electrical and electronic engineering; Nanostructures.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Comparative Study on the Effect of Substrate Structure on Electrochemical Performance and Stability of Electrodeposited Platinum and Iridium Oxide Coatings for Neural Electrodes.Micromachines (Basel). 2023 Dec 29;15(1):70. doi: 10.3390/mi15010070. Micromachines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38258189 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemical and biological characterization of thin-film platinum-iridium alloy electrode coatings: a chronic in vivo study.J Neural Eng. 2020 Jun 22;17(3):036012. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ab933d. J Neural Eng. 2020. PMID: 32408281
-
Electrochemical and mechanical performance of reduced graphene oxide, conductive hydrogel, and electrodeposited Pt-Ir coated electrodes: an active in vitro study.J Neural Eng. 2019 Dec 23;17(1):016015. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ab5163. J Neural Eng. 2019. PMID: 31652427
-
Deciphering platinum dissolution in neural stimulation electrodes: Electrochemistry or biology?Biomaterials. 2024 Sep;309:122575. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2024.122575. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Biomaterials. 2024. PMID: 38677220 Review.
-
Electrochemical and Electrophysiological Performance of Platinum Electrodes Within the Ninety-Nine-Electrode Stimulating Nerve Cuff.Artif Organs. 2015 Oct;39(10):886-96. doi: 10.1111/aor.12625. Artif Organs. 2015. PMID: 26471140 Review.
Cited by
-
Finite element analysis of electric field distribution during direct current stimulation of the spinal cord: Implications for device design.APL Bioeng. 2023 Nov 2;7(4):046109. doi: 10.1063/5.0163264. eCollection 2023 Dec. APL Bioeng. 2023. PMID: 37928641 Free PMC article.
-
Design, Fabrication, and Implantation of Invasive Microelectrode Arrays as in vivo Brain Machine Interfaces: A Comprehensive Review.J Manuf Process. 2024 Sep 30;126:185-207. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2024.07.100. Epub 2024 Jul 31. J Manuf Process. 2024. PMID: 39185373
-
Sustainability inspired fabrication of next generation neurostimulation and cardiac rhythm management electrodes via reactive hierarchical surface restructuring.Microsyst Nanoeng. 2024 Sep 9;10(1):125. doi: 10.1038/s41378-024-00754-w. Microsyst Nanoeng. 2024. PMID: 39251609 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparative Study on the Effect of Substrate Structure on Electrochemical Performance and Stability of Electrodeposited Platinum and Iridium Oxide Coatings for Neural Electrodes.Micromachines (Basel). 2023 Dec 29;15(1):70. doi: 10.3390/mi15010070. Micromachines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38258189 Free PMC article.
-
Manufacturing Processes of Implantable Microelectrode Array for In Vivo Neural Electrophysiological Recordings and Stimulation: A State-Of-the-Art Review.J Micro Nanomanuf. 2022 Dec 1;10(4):041001. doi: 10.1115/1.4063179. Epub 2023 Oct 9. J Micro Nanomanuf. 2022. PMID: 37860671 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cowley A, Woodward B. A healthy future: platinum in medical applications. Platin. Met. Rev. 2011;55:98–107. doi: 10.1595/147106711X566816. - DOI
-
- Vedam-Mai, V. et al. Proceedings of the eighth annual deep brain stimulation think tank: advances in optogenetics, ethical issues affecting DBS Research, neuromodulatory approaches for depression, adaptive neurostimulation, and emerging DBS technologies. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 15, 765150 (2021). - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
