Lysine Acetyltransferases and Their Role in AR Signaling and Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 36060957
- PMCID: PMC9428678
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.886594
Lysine Acetyltransferases and Their Role in AR Signaling and Prostate Cancer
Abstract
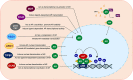
The development and growth of a normal prostate gland, as well as its physiological functions, are regulated by the actions of androgens through androgen receptor (AR) signaling which drives multiple cellular processes including transcription, cellular proliferation, and apoptosis in prostate cells. Post-translational regulation of AR plays a vital role in directing its cellular activities via modulating its stability, nuclear localization, and transcriptional activity. Among various post-translational modifications (PTMs), acetylation is an essential PTM recognized in AR and is governed by the regulated actions of acetyltransferases and deacetyltransferases. Acetylation of AR has been identified as a critical step for its activation and depending on the site of acetylation, the intracellular dynamics and activity of the AR can be modulated. Various acetyltransferases such as CBP, p300, PCAF, TIP60, and ARD1 that are known to acetylate AR, may directly coactivate the AR transcriptional function or help to recruit additional coactivators to functionally regulate the transcriptional activity of the AR. Aberrant expression of acetyltransferases and their deregulated activities have been found to interfere with AR signaling and play a key role in development and progression of prostatic diseases, including prostate cancer (PCa). In this review, we summarized recent research advances aimed at understanding the role of various lysine acetyltransferases (KATs) in the regulation of AR activity at the level of post-translational modifications in normal prostate physiology, as well as in development and progression of PCa. Considering the critical importance of KATs in modulating AR activity in physiological and patho-physiological context, we further discussed the potential of targeting these enzymes as a therapeutic option to treat AR-related pathology in combination with hormonal therapy.
Keywords: GCN5; HBO1; P300; PCAF; TIP60; androgen receptor; lysine acetyltransferases; prostate cancer.
Copyright © 2022 Jaiswal, Agarwal and Gupta.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Androgen receptor signalling in prostate cancer: the functional consequences of acetylation.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:862125. doi: 10.1155/2011/862125. Epub 2010 Dec 28. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21274273 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of p300 histone acetyltransferase activity and acetylation of the androgen receptor by bombesin in prostate cancer cells.Oncogene. 2006 Mar 30;25(14):2011-21. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209231. Oncogene. 2006. PMID: 16434977
-
Inactivation of androgen-induced regulator ARD1 inhibits androgen receptor acetylation and prostate tumorigenesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Feb 21;109(8):3053-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1113356109. Epub 2012 Feb 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22315407 Free PMC article.
-
ARD1/NAA10 acetylation in prostate cancer.Exp Mol Med. 2018 Jul 27;50(7):1-8. doi: 10.1038/s12276-018-0107-0. Exp Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30054487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone Lysine and Genomic Targets of Histone Acetyltransferases in Mammals.Bioessays. 2018 Oct;40(10):e1800078. doi: 10.1002/bies.201800078. Epub 2018 Aug 24. Bioessays. 2018. PMID: 30144132 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting epigenetic regulators to overcome drug resistance in cancers.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Feb 17;8(1):69. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01341-7. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 36797239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The epigenetic function of androgen receptor in prostate cancer progression.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Mar 21;11:1083486. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1083486. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37025180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small-molecule TIP60 inhibitors enhance regulatory T cell induction through TIP60-P300 acetylation crosstalk.iScience. 2023 Nov 19;26(12):108491. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108491. eCollection 2023 Dec 15. iScience. 2023. PMID: 38094248 Free PMC article.
-
SHP2 as a primordial epigenetic enzyme expunges histone H3 pTyr-54 to amend androgen receptor homeostasis.Nat Commun. 2024 Jul 4;15(1):5629. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49978-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38965223 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic (De)regulation in Prostate Cancer.Cancer Treat Res. 2023;190:321-360. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-45654-1_10. Cancer Treat Res. 2023. PMID: 38113006 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

