Genetic tagging of the adenosine A2A receptor reveals its heterogeneous expression in brain regions
- PMID: 36059431
- PMCID: PMC9434489
- DOI: 10.3389/fnana.2022.978641
Genetic tagging of the adenosine A2A receptor reveals its heterogeneous expression in brain regions
Abstract
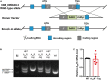
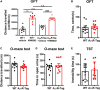
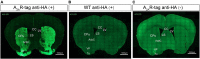
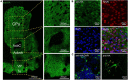
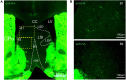
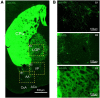
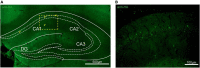
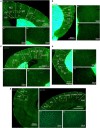
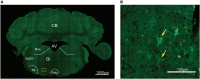
The adenosine A2A receptor (A2AR), a G protein-coupled receptor, is involved in numerous and varied physiological and pathological processes, including inflammation, immune responses, blood flow, and neurotransmission. Accordingly, it has become an important drug target for the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders. However, the exact brain distribution of A2AR in regions outside the striatum that display relatively low levels of endogenous A2AR expression has hampered the exploration of A2AR functions under both physiological and pathological conditions. To further study the detailed distribution of the A2AR in low-expression regions, we have generated A2AR knock-in mice in which the 3xHA-2xMyc epitope tag sequence was fused to the C-terminus of A2AR (A2AR-tag mice) via CRISPR/Cas9 technology. Here, using CRISPR/Cas9 technology, we have generated A2AR knock-in mice in which the 3xHA-2xMyc epitope tag sequence was fused to the C-terminus of A2AR (A2AR-tag mice). The A2AR-tag mice exhibited normal locomotor activity and emotional state. Consistent with previous studies, A2AR fluorescence was widely detected in the striatum, nucleus accumbens, and olfactory tubercles, with numerous labeled cells being evident in these regions in the A2AR-tag mouse. Importantly, we also identified the presence of a few but clearly labeled cells in heterogeneous brain regions where A2AR expression has not previously been unambiguously detected, including the lateral septum, hippocampus, amygdala, cerebral cortex, and gigantocellular reticular nucleus. The A2AR-tag mouse represents a novel useful genetic tool for monitoring the expression of A2AR and dissecting its functions in brain regions other than the striatum.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR); adenosine A2A receptor (A2AR); knock-in mice; lateral septum (LS); striatum.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Li, Song, Sun, Deng, Lin, Zeng, Qiu, Lin, Guo, Chen and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors YZ and CQ were employed by Shanghai Pregen Biotechnology Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gene dose effect reveals no Gs-coupled A2A adenosine receptor reserve in murine T-lymphocytes: studies of cells from A2A-receptor-gene-deficient mice.Biochem J. 2001 Feb 15;354(Pt 1):123-30. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3540123. Biochem J. 2001. PMID: 11171087 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of adenosine A2a receptors gene in the olfactory bulb and spinal cord of rat and mouse.Neurosci Lett. 1999 Feb 19;261(3):189-91. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(99)00022-1. Neurosci Lett. 1999. PMID: 10081981
-
Genetic and pharmacological inactivation of adenosine A2A receptor reveals an Egr-2-mediated transcriptional regulatory network in the mouse striatum.Physiol Genomics. 2005 Sep 21;23(1):89-102. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00068.2005. Epub 2005 Jul 26. Physiol Genomics. 2005. PMID: 16046619
-
Allosteric mechanisms within the adenosine A2A-dopamine D2 receptor heterotetramer.Neuropharmacology. 2016 May;104:154-60. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.05.028. Epub 2015 Jun 4. Neuropharmacology. 2016. PMID: 26051403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Allosteric Interactions between Adenosine A2A and Dopamine D2 Receptors in Heteromeric Complexes: Biochemical and Pharmacological Characteristics, and Opportunities for PET Imaging.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 9;22(4):1719. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041719. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33572077 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lateral septum adenosine A2A receptors control stress-induced depressive-like behaviors via signaling to the hypothalamus and habenula.Nat Commun. 2023 Apr 5;14(1):1880. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37601-x. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37019936 Free PMC article.
-
CD73-Mediated Formation of Extracellular Adenosine Is Responsible for Adenosine A2A Receptor-Mediated Control of Fear Memory and Amygdala Plasticity.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 24;23(21):12826. doi: 10.3390/ijms232112826. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361618 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocytic inhibition of lateral septal neurons promotes diverse stress responses.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 21;15(1):10091. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54376-x. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39572547 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alcada-Morais S., Goncalves N., Moreno-Juan V., Andres B., Ferreira S., Marques J. M., et al. (2021). Adenosine A(2A) receptors contribute to the radial migration of cortical projection neurons through the regulation of neuronal polarization and axon formation. Cereb. Cortex 31 5652–5663. 10.1093/cercor/bhab188 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Angulo E., Casadó V., Mallol J., Canela E. I., Viñals F., Ferrer I., et al. (2003). A1 adenosine receptors accumulate in neurodegenerative structures in Alzheimer disease and mediate both amyloid precursor protein processing and tau phosphorylation and translocation. Brain Pathol. 13 440–451. 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2003.tb00475.x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baraldi S., Baraldi P. G., Oliva P., Toti K. S., Ciancetta A., Jacobson K. A. (2018). “A2A adenosine receptor: Structures, modeling, and medicinal chemistry,” in The Adenosine Receptors, ed. Borea P., Varani K., Gessi S., Merighi S., Vincenzi F. (Totowa, NJ: Humana Press; ), 91–136.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

