ICOS is upregulated on T cells following radiation and agonism combined with radiation results in enhanced tumor control
- PMID: 36056093
- PMCID: PMC9440216
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-19256-8
ICOS is upregulated on T cells following radiation and agonism combined with radiation results in enhanced tumor control
Abstract
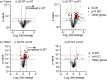
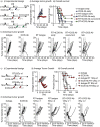
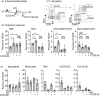
Multiple preclinical studies have shown improved outcomes when radiation therapy is combined with immune modulating antibodies. However, to date, many of these promising results have failed to translate to successful clinical studies. This led us to explore additional checkpoint and co-stimulatory pathways that may be regulated by radiation therapy. Here, we demonstrate that radiation increases the expression of inducible T cell co-stimulator (ICOS) on both CD4 and CD8 T cells in the blood following treatment. Moreover, when we combined a novel ICOS agonist antibody with radiation we observed durable cures across multiple tumor models and mouse strains. Depletion studies revealed that CD8 T cells were ultimately required for treatment efficacy, but CD4 T cells and NK cells also partially contributed to tumor control. Phenotypic analysis showed that the combination therapy diminished the increased infiltration of regulatory T cells into the tumor that typically occurs following radiation alone. Finally, we demonstrate in a poorly immunogenic pancreatic tumor model which is resistant to combined radiation and anti-PD1 checkpoint blockade that the addition of this novel ICOS agonist antibody to the treatment regimen results in tumor control. These findings identify ICOS as part of a T cell pathway that is modulated by radiation and targeting this pathway with a novel ICOS antibody results in durable tumor control in preclinical models.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
MR Crittenden reports research support from Jounce Therapeutics during the course of this study and also receives research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb and VIR that is not related to the subject of this manuscript. MJ Gough reports research support from Jounce Therapeutics during the course of this study and receives funding from Bristol Myers Squibb and VIR that is not related to the subject of this manuscript. M Gostissa is an employee and owns stock of Jounce Therapeutics. CJ. Harvey was an employee of Jounce Therapeutics during the time of study conduct. TB,JB,SB and GK have nothing to disclose and no conflicts of interest.
Figures


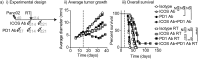
Similar articles
-
Immuno-PET Monitoring of CD8+ T Cell Infiltration Post ICOS Agonist Antibody Treatment Alone and in Combination with PD-1 Blocking Antibody Using a 89Zr Anti-CD8+ Mouse Minibody in EMT6 Syngeneic Tumor Mouse.Mol Imaging Biol. 2023 Jun;25(3):528-540. doi: 10.1007/s11307-022-01781-7. Epub 2022 Oct 20. Mol Imaging Biol. 2023. PMID: 36266600 Free PMC article.
-
ICOS agonism by JTX-2011 (vopratelimab) requires initial T cell priming and Fc cross-linking for optimal T cell activation and anti-tumor immunity in preclinical models.PLoS One. 2020 Sep 24;15(9):e0239595. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0239595. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32970735 Free PMC article.
-
PD-1 blockade augments humoral immunity through ICOS-mediated CD4+ T cell instruction.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Jan;66:127-138. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.10.045. Epub 2018 Nov 16. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30448635
-
Inducible Co-Stimulator (ICOS) as a potential therapeutic target for anti-cancer therapy.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018 Apr;22(4):343-351. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2018.1444753. Epub 2018 Mar 1. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018. PMID: 29468927 Review.
-
Role of Inducible Co-Stimulator (ICOS) in cancer immunotherapy.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2020 Feb;20(2):141-150. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2020.1693540. Epub 2019 Nov 28. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2020. PMID: 31738626 Review.
Cited by
-
Fluorescence tracking demonstrates T cell recirculation is transiently impaired by radiation therapy to the tumor.Sci Rep. 2024 May 24;14(1):11909. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-62871-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38789721 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of activation-induced markers (AIM) in porcine T cells by flow cytometry.Front Vet Sci. 2024 May 29;11:1390486. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1390486. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38868498 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of CD8+ T Cell Responses by Radiotherapy-Current Evidence and Rationale for Combination with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 24;24(23):16691. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316691. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The immunogenic radiation and new players in immunotherapy and targeted therapy for head and neck cancer.Front Oral Health. 2023 Jul 11;4:1180869. doi: 10.3389/froh.2023.1180869. eCollection 2023. Front Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 37496754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiation-induced tumor immune microenvironments and potential targets for combination therapy.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 May 19;8(1):205. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01462-z. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37208386 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

