Pre-exposure to mRNA-LNP inhibits adaptive immune responses and alters innate immune fitness in an inheritable fashion
- PMID: 36054264
- PMCID: PMC9477420
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010830
Pre-exposure to mRNA-LNP inhibits adaptive immune responses and alters innate immune fitness in an inheritable fashion
Abstract
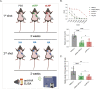
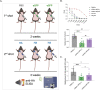
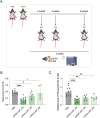
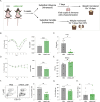
Hundreds of millions of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-LNP vaccine doses have already been administered to humans. However, we lack a comprehensive understanding of the immune effects of this platform. The mRNA-LNP-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccine is highly inflammatory, and its synthetic ionizable lipid component responsible for the induction of inflammation has a long in vivo half-life. Since chronic inflammation can lead to immune exhaustion and non-responsiveness, we sought to determine the effects of pre-exposure to the mRNA-LNP on adaptive immune responses and innate immune fitness. We found that pre-exposure to mRNA-LNPs or LNP alone led to long-term inhibition of the adaptive immune response, which could be overcome using standard adjuvants. On the other hand, we report that after pre-exposure to mRNA-LNPs, the resistance of mice to heterologous infections with influenza virus increased while resistance to Candida albicans decreased. The diminished resistance to Candida albicans correlated with a general decrease in blood neutrophil percentages. Interestingly, mice pre-exposed to the mRNA-LNP platform can pass down the acquired immune traits to their offspring, providing better protection against influenza. In summary, the mRNA-LNP vaccine platform induces long-term unexpected immunological changes affecting both adaptive immune responses and heterologous protection against infections. Thus, our studies highlight the need for more research to determine this platform's true impact on human health.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Update of
-
Pre-exposure to mRNA-LNP inhibits adaptive immune responses and alters innate immune fitness in an inheritable fashion.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2022 Aug 20:2022.03.16.484616. doi: 10.1101/2022.03.16.484616. bioRxiv. 2022. Update in: PLoS Pathog. 2022 Sep 2;18(9):e1010830. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010830 PMID: 36032972 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Pre-exposure to mRNA-LNP inhibits adaptive immune responses and alters innate immune fitness in an inheritable fashion.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2022 Aug 20:2022.03.16.484616. doi: 10.1101/2022.03.16.484616. bioRxiv. 2022. Update in: PLoS Pathog. 2022 Sep 2;18(9):e1010830. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010830 PMID: 36032972 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Delivery and Expression of mRNA in the Secondary Lymphoid Organs Drive Immune Responses to Lipid Nanoparticle-mRNA Vaccines after Intramuscular Injection.Mol Pharm. 2023 Aug 7;20(8):3876-3885. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.2c01024. Epub 2023 Jul 26. Mol Pharm. 2023. PMID: 37491979 Free PMC article.
-
Langerhans cells and cDC1s play redundant roles in mRNA-LNP induced protective anti-influenza and anti-SARS-CoV-2 immune responses.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Jan 24;18(1):e1010255. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010255. eCollection 2022 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35073387 Free PMC article.
-
From influenza to COVID-19: Lipid nanoparticle mRNA vaccines at the frontiers of infectious diseases.Acta Biomater. 2021 Sep 1;131:16-40. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.06.023. Epub 2021 Jun 18. Acta Biomater. 2021. PMID: 34153512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemistry of Lipid Nanoparticles for RNA Delivery.Acc Chem Res. 2022 Jan 4;55(1):2-12. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00544. Epub 2021 Dec 1. Acc Chem Res. 2022. PMID: 34850635 Review.
Cited by
-
From Bench to Bedside: Implications of Lipid Nanoparticle Carrier Reactogenicity for Advancing Nucleic Acid Therapeutics.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Jul 31;16(8):1088. doi: 10.3390/ph16081088. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37631003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recommendation for broad use of Covid-19 mRNA vaccine boosters due to waning vaccine effectiveness is taking the easy way out.J Infect. 2023 Mar;86(3):256-308. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2022.12.019. Epub 2022 Dec 24. J Infect. 2023. PMID: 36574907 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Non-neutralizing functions in anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies.Biomed J. 2024 Feb;47(1):100666. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2023.100666. Epub 2023 Sep 29. Biomed J. 2024. PMID: 37778697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased Risk of Thyroid Eye Disease Following Covid-19 Vaccination.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2024 Jan 18;109(2):516-526. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgad501. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2024. PMID: 37622279 Free PMC article.
-
"Don't Look Up" Your Science-Herd Immunity or Herd Mentality?Microorganisms. 2022 Jul 20;10(7):1463. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10071463. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35889182 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alameh M-G, Tombácz I, Bettini E, Lederer K, Ndeupen S, Sittplangkoon C, et al.. Lipid nanoparticles enhance the efficacy of mRNA and protein subunit vaccines by inducing robust T follicular helper cell and humoral responses. Immunity. 2021;54: 2877–2892.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.11.001 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

