Fluoro-recognition: New in vivo fluorescent assay for toluene dioxygenase probing induction by and metabolism of polyfluorinated compounds
- PMID: 36054238
- PMCID: PMC9828342
- DOI: 10.1111/1462-2920.16187
Fluoro-recognition: New in vivo fluorescent assay for toluene dioxygenase probing induction by and metabolism of polyfluorinated compounds
Abstract
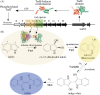
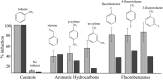
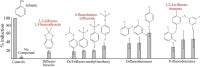
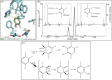
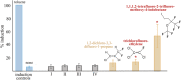
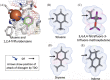
The present study examined the regulatory and metabolic response of the aromatic degrader Pseudomonas putida F1 and its tod operon, controlling toluene degradation, to fluorinated aromatic and aliphatic compounds. The tod operon is upregulated by inducer binding to the TodS sensing domain of a two-component regulator. The induced enzymes include toluene dioxygenase that initiates catabolic assimilation of benzenoid hydrocarbons. Toluene dioxygenase was shown to oxidize 6-fluoroindole to a meta-stable fluorescent product, 6-fluoroindoxyl. The fluorescent output allowed monitoring relative levels of tod operon induction in whole cells using microtiter well plates. Mono- and polyfluorinated aromatic compounds were shown to induce toluene dioxygenase, in some cases to a greater extent than compounds serving as growth substrates. Compounds that are oxidized by toluene dioxygenase and undergoing defluorination were shown to induce their own metabolism. 1,2,4-Trifluorobenzene caused significant induction and computational modelling indicated productive binding to the TodS sensor domain of the TodST regulator. Toluene dioxygenase also showed preferential binding of 1,2,4-trifluorobenzene such that defluorination was favoured. Fluorinated aliphatic compounds were shown to induce toluene dioxygenase. An aliphatic ether with seven fluorine atoms, 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoro-2-trifluoromethoxy-4-iodobutane (TTIB), was an excellent inducer of toluene dioxygenase activity and shown to undergo transformation in cultures of P. putida F1.
© 2022 The Authors. Environmental Microbiology published by Society for Applied Microbiology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with this manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Unexpected Mechanism of Biodegradation and Defluorination of 2,2-Difluoro-1,3-Benzodioxole by Pseudomonas putida F1.mBio. 2021 Dec 21;12(6):e0300121. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03001-21. Epub 2021 Nov 16. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34781746 Free PMC article.
-
Expansion of growth substrate range in Pseudomonas putida F1 by mutations in both cymR and todS, which recruit a ring-fission hydrolase CmtE and induce the tod catabolic operon, respectively.Microbiology (Reading). 2003 Mar;149(Pt 3):795-805. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.26046-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2003. PMID: 12634347
-
Catabolite repression of the TodS/TodT two-component system and effector-dependent transphosphorylation of TodT as the basis for toluene dioxygenase catabolic pathway control.J Bacteriol. 2010 Aug;192(16):4246-50. doi: 10.1128/JB.00379-10. Epub 2010 Jun 11. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20543072 Free PMC article.
-
Toluene metabolism by the solvent-tolerant Pseudomonas putida DOT-T1 strain, and its role in solvent impermeabilization.Gene. 1999 May 17;232(1):69-76. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(99)00113-4. Gene. 1999. PMID: 10333523
-
Gene components responsible for discrete substrate specificity in the metabolism of biphenyl (bph operon) and toluene (tod operon).J Bacteriol. 1993 Aug;175(16):5224-32. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.16.5224-5232.1993. J Bacteriol. 1993. PMID: 8349562 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Contrasting Mechanisms of Aromatic and Aryl-Methyl Substituent Hydroxylation by the Rieske Monooxygenase Salicylate 5-Hydroxylase.Biochemistry. 2023 Jan 17;62(2):507-523. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.2c00610. Epub 2022 Dec 30. Biochemistry. 2023. PMID: 36583545 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ameria, S.P.L. , Jung, H.S. , Kim, H.S. , Han, S.S. , Kim, H.S. & Lee, J.H. (2015) Characterization of a flavin‐containing monooxygenase from Corynebacterium glutamicum and its application to production of indigo and indirubin. Biotechnology Letters, 37, 1637–1644. - PubMed
-
- Bhat, A.P. , Mundhenke, T.F. , Whiting, Q.T. , Peterson, A.A. , Pomerantz, W.C. & Arnold, W.A. (2022) Tracking fluorine during aqueous photolysis and advanced UV treatment of fluorinated phenols and pharmaceuticals using a combined 19F‐NMR, chromatography, and mass spectrometry approach. ACS Environmental Au, 2, 242–252. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Božilović, J. , Bats, J.W. & Engels, J.W. (2007) Synthesis and structure of fluoroindole nucleosides. Canadian Journal of Chemistry, 85, 283–292.
-
- Britton, R. , Gouverneur, V. , Lin, J.H. , Meanwell, M. , Ni, C. , Pupo, G. et al. (2021) Contemporary synthetic strategies in organofluorine chemistry. Nature Reviews Methods Primers, 1, 1–22.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

