A nomogram for predicting good response after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced rectal cancer: a retrospective, double-center, cohort study
- PMID: 36048198
- PMCID: PMC9560928
- DOI: 10.1007/s00384-022-04247-y
A nomogram for predicting good response after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced rectal cancer: a retrospective, double-center, cohort study
Abstract
Aim: The purpose of this study was to explore the clinical factors associated with achieving good response after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT) in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer (LARC) and to develop and validate a nomogram.
Methods: A total of 1724 consecutive LARC patients treated at Fujian Medical University Union Hospital from January 2010 to December 2021 were retrospectively evaluated as the training cohort; 267 consecutive LARC patients treated at Zhangzhou Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University during the same period were evaluated as the external 2 cohorts. Based on the pathological results after radical surgery, treatment response was defined as follows: good response, stage ypT0∼2N0M0 and poor response, ypT3∼4N0M0 and/or N positive. Independent influencing factors were analyzed by logistic regression, a nomogram was developed and validated, and the model was evaluated using internal and external data cohorts for validation.
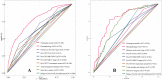
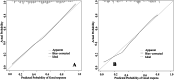
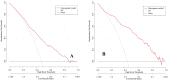
Results: In the training cohort, 46.6% of patients achieved good response after nCRT combined with radical surgery. The rate of the retained anus was higher in the good response group (93.5% vs. 90.7%, P < 0.001). Cox regression analysis showed that the risk of overall survival and disease-free survival was significantly lower among good response patients than poor response patients, HR = 0.204 (95%CI: 0.146-0.287). Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed an independent association with 9 clinical factors, including histopathology, and a nomogram with an excellent predictive response was developed accordingly. The C-index of the predictive accuracy of the nomogram was 0.764 (95%CI: 0.742-0.786), the internal validation of the 200 bootstrap replication mean C-index was 0.764, and the external validation cohort showed an accuracy C-index of 0.789 (95%CI: 0.734-0.844), with good accuracy of the model.
Conclusion: We identified factors associated with achieving good response in LARC after treatment with nCRT and developed a nomogram to contribute to clinical decision-making.
Keywords: Good response; Locally advanced rectal cancer; Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy; Nomogram.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nomograms for predicting pathological response to neoadjuvant treatments in patients with rectal cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Jan 7;25(1):118-137. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i1.118. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30643363 Free PMC article.
-
A nomogram to predict distant metastasis after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy and radical surgery in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer.J Surg Oncol. 2017 Mar;115(4):462-469. doi: 10.1002/jso.24522. Epub 2017 Jan 20. J Surg Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28105657
-
Development and validation of neoadjuvant rectal score-based signature nomograms to predict overall survival and disease-free survival in locally advanced rectal cancer: a retrospective, double center, cohort study.Int J Clin Oncol. 2023 Feb;28(2):268-279. doi: 10.1007/s10147-022-02281-y. Epub 2022 Dec 19. Int J Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36534264
-
Impact of body mass index on treatment outcome of neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2017 Oct;43(10):1828-1834. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2017.07.022. Epub 2017 Aug 10. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28888798 Review.
-
Nucleic acid-based markers of response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer.Surg Oncol. 2022 May;41:101743. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2022.101743. Epub 2022 Mar 24. Surg Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35358913 Review.
Cited by
-
A dynamic nomogram for predicting pathologic complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer.Cancer Med. 2024 Jun;13(11):e7251. doi: 10.1002/cam4.7251. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 38819440 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a multi-modal ultrasomics model to predict response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer.BMC Med Imaging. 2024 Mar 18;24(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s12880-024-01237-0. BMC Med Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38500022 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of comprehensive nomograms from the SEER database for predicting early mortality in metastatic rectal cancer patients.BMC Gastroenterol. 2024 Feb 26;24(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s12876-024-03178-y. BMC Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38408896 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2019QH1276/Startup Fund for Scientific Research, Fujian Medical University
- 2020J011030/Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province
- B20062DS/Medical Science Research Foundation of Beijing Medical and Health Foundation
- 2020CXA025/Fujian provincial health technology project
- X-J-2018-004/Bethune Charitable Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

