Epigenetics and its role in effecting agronomical traits
- PMID: 36046583
- PMCID: PMC9421166
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.925688
Epigenetics and its role in effecting agronomical traits
Abstract
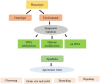
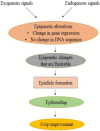
Climate-resilient crops with improved adaptation to the changing climate are urgently needed to feed the growing population. Hence, developing high-yielding crop varieties with better agronomic traits is one of the most critical issues in agricultural research. These are vital to enhancing yield as well as resistance to harsh conditions, both of which help farmers over time. The majority of agronomic traits are quantitative and are subject to intricate genetic control, thereby obstructing crop improvement. Plant epibreeding is the utilisation of epigenetic variation for crop development, and has a wide range of applications in the field of crop improvement. Epigenetics refers to changes in gene expression that are heritable and induced by methylation of DNA, post-translational modifications of histones or RNA interference rather than an alteration in the underlying sequence of DNA. The epigenetic modifications influence gene expression by changing the state of chromatin, which underpins plant growth and dictates phenotypic responsiveness for extrinsic and intrinsic inputs. Epigenetic modifications, in addition to DNA sequence variation, improve breeding by giving useful markers. Also, it takes epigenome diversity into account to predict plant performance and increase crop production. In this review, emphasis has been given for summarising the role of epigenetic changes in epibreeding for crop improvement.
Keywords: agronomic traits; epialleles; epigenetic; improvement; plant species.
Copyright © 2022 Gupta and Salgotra.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epigenomics in stress tolerance of plants under the climate change.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Jul;50(7):6201-6216. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08539-6. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37294468 Review.
-
Epigenetic variation in maize agronomical traits for breeding and trait improvement.J Genet Genomics. 2025 Mar;52(3):307-318. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2024.01.006. Epub 2024 Feb 3. J Genet Genomics. 2025. PMID: 38310944 Review.
-
Epigenetics for Crop Improvement in Times of Global Change.Biology (Basel). 2021 Aug 11;10(8):766. doi: 10.3390/biology10080766. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Will epigenetics be a key player in crop breeding?Front Plant Sci. 2022 Sep 30;13:958350. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.958350. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36247549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Epigenetics and the improvement of crop plants].Postepy Biochem. 2024 Sep 17;70(3):371-381. doi: 10.18388/pb.2021_514. Print 2024 Sep 30. Postepy Biochem. 2024. PMID: 39365576 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Multi-Omics Uncover the Mechanism of Wheat under Heavy Metal Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 15;23(24):15968. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415968. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The creation of autotetraploid provides insights into critical features of DNA methylome changes after genome doubling in water spinach (Ipomoea aquatica Forsk).Front Plant Sci. 2023 Apr 14;14:1155531. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1155531. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37123819 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic variation: A major player in facilitating plant fitness under changing environmental conditions.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Oct 18;10:1020958. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1020958. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36340045 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

