An overview of the potential anticancer properties of cardamonin
- PMID: 36046386
- PMCID: PMC9400778
- DOI: 10.37349/etat.2020.00026
An overview of the potential anticancer properties of cardamonin
Abstract
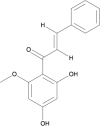
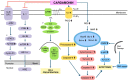
Cancer is one of the leading causes of mortality, contributing to 9.6 million deaths globally in 2018 alone. Although several cancer treatments exist, they are often associated with severe side effects and high toxicities, leaving room for significant advancements to be made in the field. In recent years, several phytochemicals from plants and natural bioresources have been extracted and tested against various human malignancies using both in vitro and in vivo preclinical model systems. Cardamonin, a chalcone extracted from the Alpinia species, is an example of a natural therapeutic agent that has anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory effects against human cancer cell lines, including breast, lung, colon, and gastric, in both in vitro culture systems as well as xenograft mouse models. Earlier, cardamonin was used as a natural medicine against stomach related issues, diarrhea, insulin resistance, nephroprotection against cisplatin treatment, vasorelaxant and antinociceptive. The compound is well-known to inhibit proliferation, migration, invasion, and induce apoptosis, through the involvement of Wnt/β-catenin, NF-κB, and PI3K/Akt pathways. The good biosafety and pharmacokinetic profiling of cardamonin satisfy it as an attractive molecule for the development of an anticancer agent. The present review has summarized the chemo-preventive ability of cardamonin as an anticancer agent against numerous human malignancies.
Keywords: Cancer; NF-κB, PI3K/Akt; Wnt/β-catenin; apoptosis; cardamonin; chalcone; proliferation.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardamonin: A new player to fight cancer via multiple cancer signaling pathways.Life Sci. 2020 Jun 1;250:117591. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117591. Epub 2020 Mar 26. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32224026 Review.
-
Cardamonin, a natural chalcone, reduces 5-fluorouracil resistance of gastric cancer cells through targeting Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway.Invest New Drugs. 2020 Apr;38(2):329-339. doi: 10.1007/s10637-019-00781-9. Epub 2019 May 17. Invest New Drugs. 2020. PMID: 31102118
-
Cardamonin inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of non-small-cell lung cancer cells by suppressing the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway.Anticancer Drugs. 2019 Mar;30(3):241-250. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000709. Anticancer Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30640793
-
An Overview of the Potential Antineoplastic Effects of Casticin.Molecules. 2020 Mar 12;25(6):1287. doi: 10.3390/molecules25061287. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32178324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardamonin induces G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis through inhibition of NF-κB and mTOR pathways in ovarian cancer.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Nov 25;12(24):25730-25743. doi: 10.18632/aging.104184. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 33234722 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Anticancer Potential of Natural Chalcones: In Vitro and In Vivo Evidence.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 19;24(12):10354. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210354. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering the Potentials of Cardamom in Cancer Prevention and Therapy: From Kitchen to Clinic.Biomolecules. 2024 Sep 18;14(9):1166. doi: 10.3390/biom14091166. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39334932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Combination of Cardamonin and Doxorubicin Selectively Affect Cell Viability of Melanoma Cells: An In Vitro Study.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jul 19;13(7):864. doi: 10.3390/antiox13070864. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061932 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of cardamonin on the growth performance, intestinal barrier function and intestinal microbiota of Danzhou chickens under heat stress.Poult Sci. 2024 Dec;103(12):104362. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104362. Epub 2024 Sep 26. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 39426223 Free PMC article.
-
Cardamonin as a p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway Activator Inhibits Human Coronavirus OC43 Infection in Human Lung Cells.Nutrients. 2023 Mar 9;15(6):1335. doi: 10.3390/nu15061335. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36986065 Free PMC article.
References
-
- GBD 2015 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388:1659–724. 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31679-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources